Eosinophilic esophagitis
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Eosinophilic esophagitis | |
|---|---|
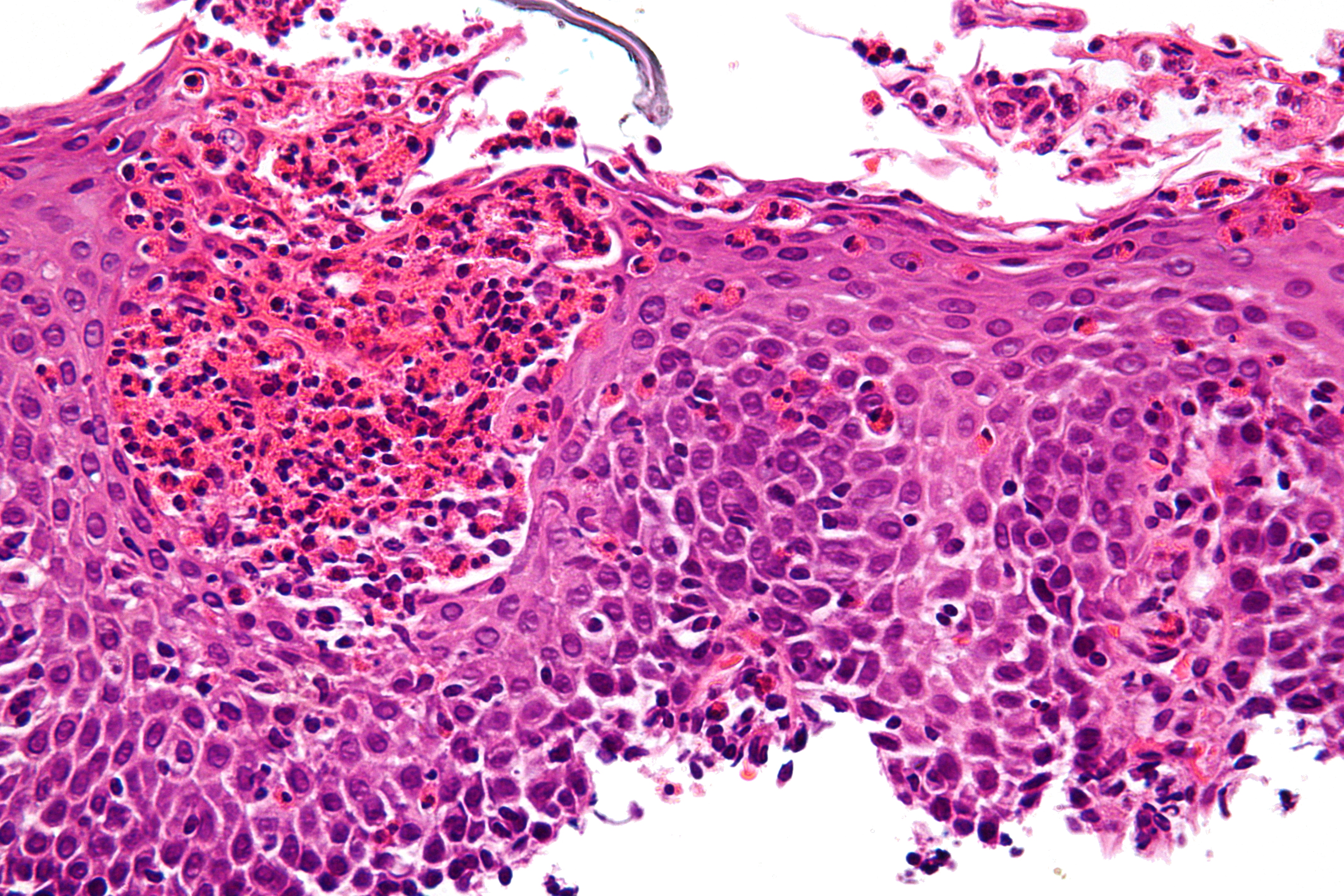
| |
| Synonyms | EoE |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Dysphagia, food impaction, chest pain, heartburn |
| Complications | Esophageal stricture, esophageal perforation |
| Onset | Childhood or adulthood |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Allergic reaction |
| Risks | Atopic dermatitis, asthma, allergic rhinitis, food allergies |
| Diagnosis | Endoscopy, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Gastroesophageal reflux disease, esophageal cancer, achalasia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Dietary management, proton pump inhibitors, topical corticosteroids |
| Medication | Fluticasone, budesonide |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | 1 in 2,000 people |
| Deaths | N/A |
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, immune system disease that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube that delivers food from the mouth to the stomach. It is characterized by a large number of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the esophagus.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The most common symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis include difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), food impaction, and persistent heartburn. Children may also experience abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and failure to thrive.
Causes[edit | edit source]
Eosinophilic esophagitis is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is often associated with other allergic conditions, such as asthma, eczema, and food allergies.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The gold standard for diagnosis is an endoscopy with biopsy, which allows for the direct visualization of the esophagus and the collection of tissue samples for microscopic examination.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis typically involves dietary modifications, medication, and in some cases, dilation of the esophagus. The goal of treatment is to reduce eosinophil levels in the esophagus, alleviate symptoms, and prevent long-term complications.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
With appropriate treatment, most individuals with eosinophilic esophagitis can lead normal lives. However, the condition is chronic and requires ongoing management to prevent recurrence of symptoms and complications.
Images[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP1 injections from $125
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program NYC and a clinic to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our W8MD's physician supervised medical weight loss centers in NYC provides expert medical guidance, and offers telemedicine options for convenience.
Why choose W8MD?
- Comprehensive care with FDA-approved weight loss medications including:
- loss injections in NYC both generic and brand names:
- weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion etc.
- Accept most insurances for visits or discounted self pay cost.
- Generic weight loss injections starting from just $125.00 for the starting dose
- In person weight loss NYC and telemedicine medical weight loss options in New York city available
- Budget GLP1 weight loss injections in NYC starting from $125.00 biweekly with insurance!
Book Your Appointment
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss, and Philadelphia medical weight loss Call (718)946-5500 for NY and 215 676 2334 for PA
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD




