Mammary secretory carcinoma
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Mammary secretory carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Secretory breast carcinoma, juvenile breast carcinoma |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Oncology, Pathology |
| Symptoms | Breast mass, nipple discharge |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Can occur at any age, including children |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | |
| Causes | Genetic mutations, including ETV6-NTRK3 fusion |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Histopathology, immunohistochemistry |
| Differential diagnosis | Invasive ductal carcinoma, ductal carcinoma in situ |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Generally favorable with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A rare type of breast cancer
Mammary secretory carcinoma is a rare type of breast cancer characterized by its unique histological appearance and clinical behavior. It was first described in children and young adults but can occur in individuals of any age. This carcinoma is notable for its indolent nature and generally favorable prognosis compared to other forms of breast cancer.
Histopathology[edit | edit source]
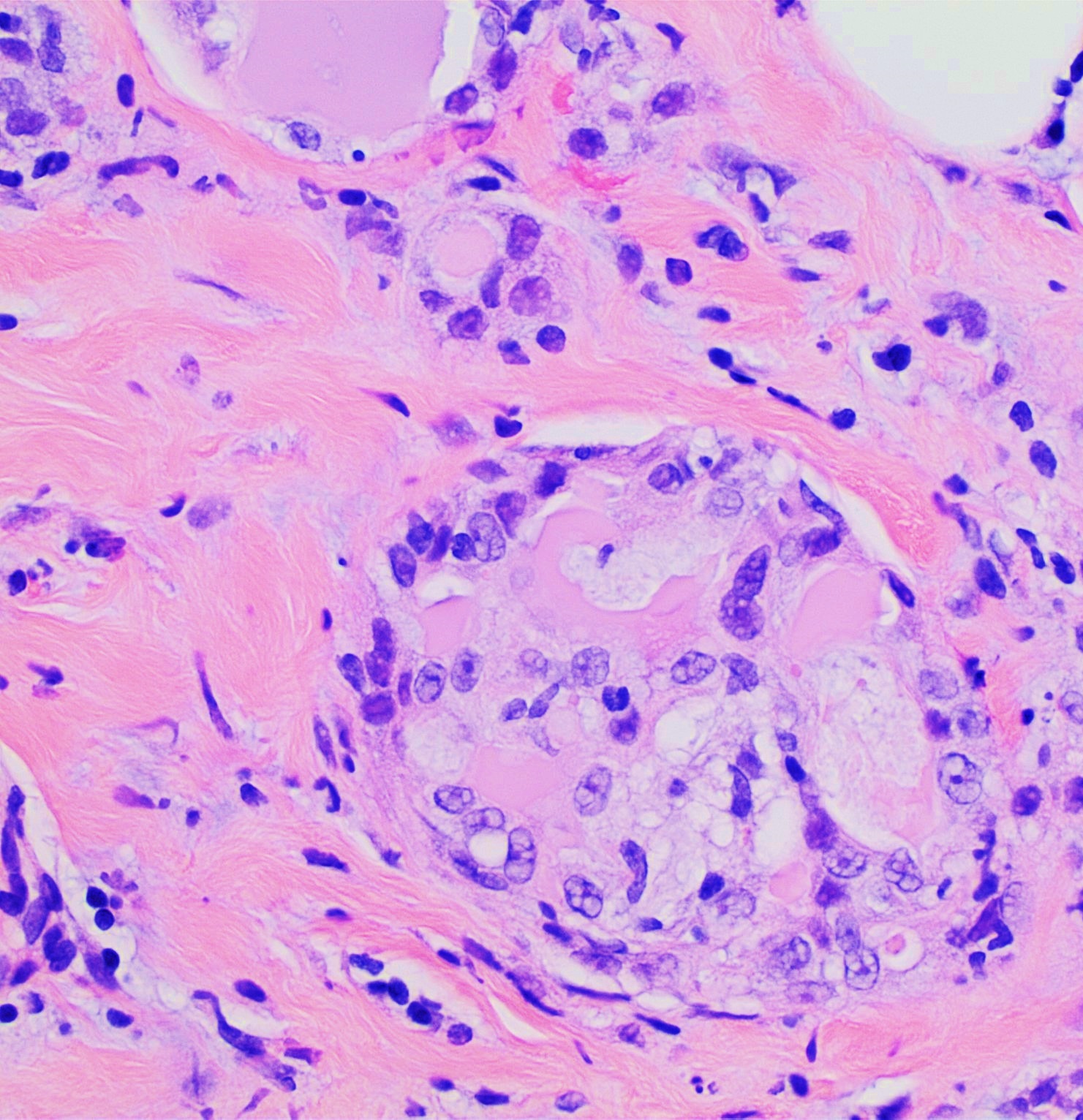
Mammary secretory carcinoma is distinguished by its histological features, which include the presence of abundant secretory material within the tumor cells. Under the microscope, the tumor exhibits a microcystic, tubular, and solid growth pattern. The cells are typically polygonal with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and vesicular nuclei. A hallmark of this carcinoma is the presence of intracellular and extracellular secretory material that stains positively with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain.
Genetic Characteristics[edit | edit source]
A defining genetic feature of mammary secretory carcinoma is the presence of the ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion. This chromosomal translocation t(12;15)(p13;q25) results in the fusion of the ETV6 gene on chromosome 12 with the NTRK3 gene on chromosome 15. This genetic alteration is also found in other types of secretory carcinomas, such as those occurring in the salivary glands.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with mammary secretory carcinoma typically present with a palpable breast mass. The tumor is often well-circumscribed and may be mistaken for a benign lesion on initial examination. Although it can occur at any age, it is more commonly diagnosed in younger individuals, including children and adolescents.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of mammary secretory carcinoma is confirmed through a combination of histopathological examination and molecular testing for the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion. Immunohistochemical staining may also be used to support the diagnosis, with the tumor cells typically expressing markers such as S-100 protein and mammaglobin.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The primary treatment for mammary secretory carcinoma is surgical excision, which may involve a lumpectomy or mastectomy depending on the size and location of the tumor. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is often performed to assess for regional lymph node involvement. Adjuvant therapies, such as radiation or chemotherapy, may be considered based on individual patient factors and the extent of disease.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for patients with mammary secretory carcinoma is generally favorable, with a high rate of long-term survival. The tumor is typically slow-growing and less likely to metastasize compared to other types of breast cancer. However, local recurrence can occur, emphasizing the importance of adequate surgical margins during initial treatment.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

