Neurogenic shock
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Neurogenic shock | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hypotension, bradycardia, warm skin |
| Complications | Organ failure, death |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Spinal cord injury, trauma |
| Risks | Cervical spine injury, high thoracic spine injury |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Hypovolemic shock, septic shock, cardiogenic shock |
| Prevention | Spinal precautions, early stabilization |
| Treatment | Intravenous fluids, vasopressors, atropine |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
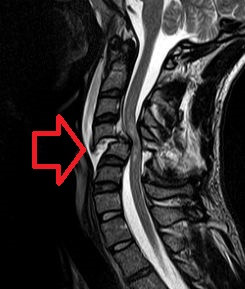
A type of shock resulting from spinal cord injury
Neurogenic shock is a type of distributive shock that occurs when there is a sudden loss of signals from the sympathetic nervous system that maintain the normal muscle tone in blood vessel walls. This condition is most commonly associated with spinal cord injury, particularly injuries to the cervical or upper thoracic spine.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
Neurogenic shock results from the disruption of the autonomic pathways within the spinal cord. The loss of sympathetic tone leads to unopposed parasympathetic nervous system activity, resulting in widespread vasodilation, decreased systemic vascular resistance, and subsequent hypotension. The heart rate may also be affected, leading to bradycardia due to the lack of sympathetic stimulation.
Causes[edit | edit source]
The primary cause of neurogenic shock is acute spinal cord injury, particularly at the cervical or high thoracic levels. Other causes may include severe head injury or conditions that affect the autonomic nervous system.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Patients with neurogenic shock may present with:
- Hypotension
- Bradycardia
- Warm, dry skin due to vasodilation
- Reduced cardiac output
- Possible respiratory failure if the injury affects the diaphragm
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of neurogenic shock is primarily clinical, based on the presence of hypotension and bradycardia following a spinal cord injury. Imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scan, are used to assess the extent of spinal cord damage.
Management[edit | edit source]
The management of neurogenic shock involves:
- Stabilization of the spine to prevent further injury
- Administration of intravenous fluids to maintain blood pressure
- Use of vasopressors to counteract vasodilation
- Atropine may be used to treat bradycardia
- Monitoring and support of respiratory function
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis of neurogenic shock depends on the severity and level of the spinal cord injury. Early recognition and management are crucial to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

