Hiatal hernia
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hiatal hernia | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Hiatus hernia |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Heartburn, regurgitation, dysphagia |
| Complications | Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), esophagitis, Barrett's esophagus |
| Onset | More common with age |
| Duration | Can be chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Obesity, pregnancy, aging, trauma |
| Risks | Obesity, smoking, pregnancy |
| Diagnosis | Endoscopy, barium swallow, esophageal manometry |
| Differential diagnosis | Peptic ulcer disease, esophageal cancer, angina |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Lifestyle changes, medication, surgery |
| Medication | Proton pump inhibitors, H2 receptor antagonists |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common, especially in those over 50 |
| Deaths | N/A |
Hiatal hernia
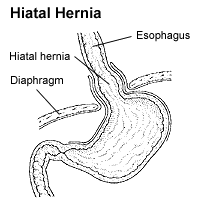
A hiatal hernia occurs when a part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm and into the chest cavity. The diaphragm is a large muscle that helps with breathing and separates the chest cavity from the abdomen. The opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes is called the hiatus. When the stomach bulges through this opening, it is referred to as a hiatal hernia.
Types[edit | edit source]
There are two main types of hiatal hernias:
- Sliding hiatal hernia: This is the most common type, where the stomach and the section of the esophagus that joins the stomach slide up into the chest through the hiatus.
- Paraesophageal hiatal hernia: This is less common but more serious. Part of the stomach pushes through the hiatus and sits next to the esophagus. This type can lead to more severe complications.
Causes[edit | edit source]
The exact cause of hiatal hernias is not always clear, but several factors may contribute, including:
- Age-related changes in the diaphragm
- Injury to the area
- Persistent and intense pressure on the surrounding muscles, such as from coughing, vomiting, or straining during bowel movements
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Many people with a hiatal hernia do not experience any symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Heartburn
- Regurgitation of food or liquids into the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest or abdominal pain
- Feeling full soon after eating
- Shortness of breath
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Hiatal hernias are often discovered during tests for other conditions. Common diagnostic methods include:
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for a hiatal hernia depends on the severity of the symptoms. Options include:
- Lifestyle changes, such as eating smaller meals, avoiding certain foods, and not lying down after eating
- Medications to reduce stomach acid, such as antacids, H2-receptor antagonists, and proton pump inhibitors
- Surgery, in severe cases, to reposition the stomach and repair the hiatus
Complications[edit | edit source]
If left untreated, a hiatal hernia can lead to complications such as:
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Esophagitis
- Strangulation of the hernia, which can cut off blood supply to the stomach
Prevention[edit | edit source]
While it may not be possible to prevent a hiatal hernia entirely, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding heavy lifting
- Eating smaller meals
- Avoiding foods and drinks that trigger heartburn
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP1 injections from $125 and up biweekly
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program NYC and a clinic to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our W8MD's physician supervised medical weight loss centers in NYC provides expert medical guidance, and offers telemedicine options for convenience.
Why choose W8MD?
- Comprehensive care with FDA-approved weight loss medications including:
- loss injections in NYC both generic and brand names:
- weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Contrave, Diethylpropion etc.
- Accept most insurances for visits or discounted self pay cost.
- Generic weight loss injections starting from just $125.00 for the starting dose
- In person weight loss NYC and telemedicine medical weight loss options in New York city available
Book Your Appointment
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss, and Philadelphia and visit Philadelphia medical weight loss Call (718)946-5500 for NY and 215 676 2334 for PA
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD






