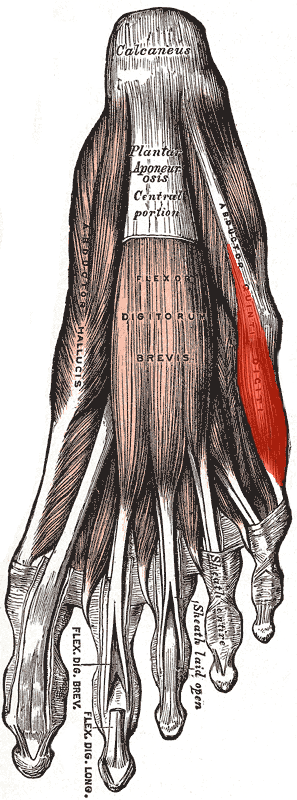
Abductor digiti minimi muscle of foot
(Redirected from Musculus abductor digiti minimi pedis)
The abductor digiti minimi muscle of the foot (Latin: musculus abductor digiti minimi pedis) is a muscle located on the lateral side of the foot. It is one of the muscles in the first layer of the sole of the foot.
Structure[edit | edit source]
The abductor digiti minimi muscle originates from the calcaneus and the plantar aponeurosis. It inserts into the lateral side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the fifth toe.
Innervation[edit | edit source]
The muscle is innervated by the lateral plantar nerve, which is a branch of the tibial nerve.
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
The blood supply to the abductor digiti minimi muscle is provided by the lateral plantar artery.
Function[edit | edit source]
The primary function of the abductor digiti minimi muscle is to abduct and flex the fifth toe. This action helps to maintain balance and stability while walking and standing.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Injury or dysfunction of the abductor digiti minimi muscle can lead to difficulties in walking and maintaining balance. Conditions such as plantar fasciitis or nerve damage can affect the performance of this muscle.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
- Sole of the foot
- Lateral plantar nerve
- Lateral plantar artery
- Calcaneus
- Plantar aponeurosis
- Fifth toe
- Tibial nerve
- Plantar fasciitis
| Muscles of the hip and human leg | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD