Basilic vein
(Redirected from Vena basilica)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
Anatomy > Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body > Cardiovascular system > Veins > Veins of the upper limb > Basilic vein
Henry Gray (1821–1865). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918.
Basilic vein[edit | edit source]
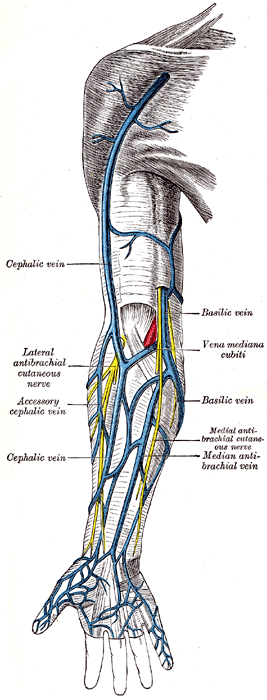
The basilic vein is a prominent superficial vein of the upper limb that drains blood from the medial side of the hand, forearm, and arm. It is one of the major superficial veins of the limb, alongside the cephalic vein.
Anatomical Course[edit | edit source]
Origin[edit | edit source]
The basilic vein arises from the dorsal venous network of the hand, specifically on the ulnar (medial) side. It begins as a continuation of the dorsal venous arch and ascends on the medial aspect of the forearm.
Forearm[edit | edit source]
As it ascends the forearm, the basilic vein runs in the subcutaneous tissue overlying the flexor muscles, often visible through the skin. It communicates with the cephalic vein via the median cubital vein, a frequent site for venipuncture. The superficial venous pattern in the forearm is highly variable, and the basilic vein forms multiple connections with unnamed tributary veins.
Arm[edit | edit source]
In the arm, the basilic vein ascends along the medial border of the biceps brachii muscle. It pierces the brachial fascia near or above the medial epicondyle of the humerus, often in the middle of the arm. Once deep, it travels alongside the brachial artery and median nerve.
At the lower border of the teres major muscle, the basilic vein unites with the brachial veins to form the axillary vein, which continues proximally to become the subclavian vein.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Venipuncture[edit | edit source]
The basilic vein, while an acceptable site for intravenous access, is less commonly used for phlebotomy due to its awkward position when the forearm is supinated. IV nurses often refer to it as the "virgin vein" because it is typically spared in routine blood draws.
Dialysis Access[edit | edit source]
In vascular surgery, the basilic vein is often utilized in the creation of an arteriovenous fistula or arteriovenous graft for patients undergoing hemodialysis. The vein's size and accessibility make it suitable for this purpose, especially when superficial veins like the cephalic vein are inadequate.
Relations[edit | edit source]
- Lies medial to the biceps brachii.
- Travels superficially before piercing the deep fascia.
- Runs with the medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
- Terminates by merging with deep veins to form the axillary vein.
Additional Images[edit | edit source]
The veins of the right axilla, anterior view.
Cross-section through the middle of the upper arm.
Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
The brachial artery and its veins.
Superficial veins on the dorsum of the hand.
Basilic vein on the forearm of a muscular adult male.
Dissection Images[edit | edit source]
| Dissection gallery |
|---|
|
See Also[edit | edit source]
- Cephalic vein
- Median cubital vein
- Axillary vein
- Venipuncture
- Hemodialysis
- Superficial veins of upper limb
External Links[edit | edit source]
- Anatomy photo:07:st-0701 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Radiology image: UpperLimb:18VenoFo from Radiology Atlas at SUNY Downstate Medical Center (need to enable Java)
- Cannulation Illustration
Gray's Anatomy[edit source]
- Gray's Anatomy Contents
- Gray's Anatomy Subject Index
- About Classic Gray's Anatomy
- Glossary of anatomy terms
Anatomy atlases (external)[edit source]
[1] - Anatomy Atlases
| Human systems and organs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Adapted from the Classic Grays Anatomy of the Human Body 1918 edition (public domain)
| Arteries and veins | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Veins of the human arm | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Human regional anatomy | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD