First-degree atrioventricular block
(Redirected from First degree atrioventricular block)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| First-degree atrioventricular block | |
|---|---|
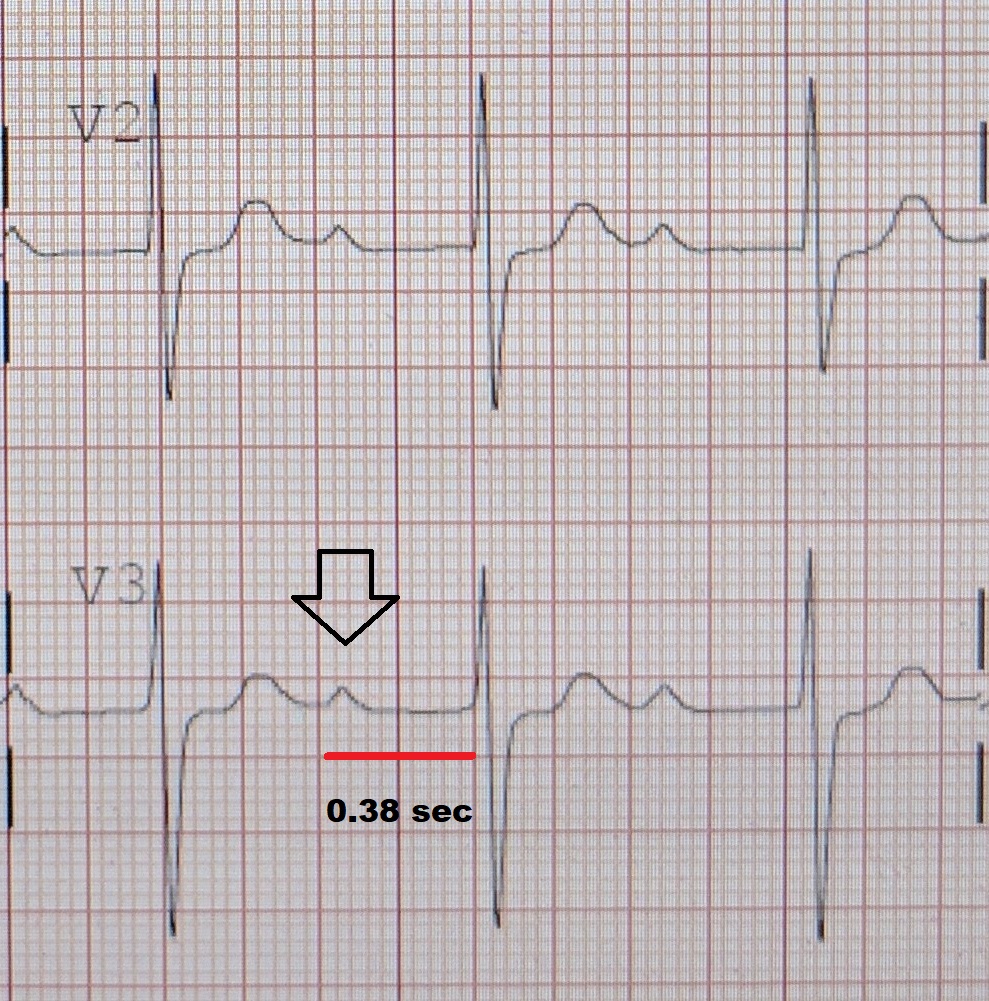
| |
| Synonyms | First-degree AV block, PR prolongation |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic, may cause bradycardia |
| Complications | Progression to higher degree atrioventricular block |
| Onset | Can occur at any age |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Vagal tone, medications (e.g., beta blockers, calcium channel blockers), myocardial infarction, Lyme disease |
| Risks | Age, heart disease, electrolyte imbalance |
| Diagnosis | Electrocardiogram (ECG) showing prolonged PR interval |
| Differential diagnosis | Second-degree atrioventricular block, third-degree atrioventricular block, bundle branch block |
| Prevention | Avoidance of causative medications, management of underlying conditions |
| Treatment | Often none required, monitoring, addressing underlying causes |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good if isolated |
| Frequency | Common, especially in older adults |
| Deaths | N/A |
First-degree atrioventricular (AV) block is a type of heart block where the electrical conduction between the atria and ventricles of the heart is delayed but not interrupted. It is the mildest form of AV block and is often asymptomatic.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
In first-degree AV block, the electrical impulse generated in the sinoatrial node is delayed at the atrioventricular node before it reaches the ventricles. This delay is reflected on an electrocardiogram (ECG) as a prolonged PR interval, which is greater than 200 milliseconds. The PR interval is the time from the onset of the P wave to the start of the QRS complex.
Causes[edit | edit source]
First-degree AV block can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Increased vagal tone
- Medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and digoxin
- Electrolyte imbalances, particularly hyperkalemia
- Myocardial ischemia or infarction
- Degenerative changes in the conduction system due to aging
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
First-degree AV block is often benign and does not require treatment. However, it can be an indicator of underlying heart disease or a precursor to more advanced forms of heart block. In some cases, it may be associated with an increased risk of atrial fibrillation and other arrhythmias.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of first-degree AV block is typically made using an ECG, which will show a prolonged PR interval. It is important to differentiate it from other types of AV block, such as second-degree and third-degree AV block, which have different clinical implications and management strategies.
Management[edit | edit source]
In most cases, no specific treatment is required for first-degree AV block. Management focuses on addressing any underlying causes, such as adjusting medications or correcting electrolyte imbalances. Regular monitoring may be recommended to ensure that the block does not progress to a more severe form.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for individuals with first-degree AV block is generally excellent, especially if there is no underlying heart disease. Most individuals live normal, healthy lives without any significant complications.
Also see[edit | edit source]
- Second-degree atrioventricular block
- Third-degree atrioventricular block
- Electrocardiogram
- Atrioventricular node
- Heart conduction system
Cardiovascular disease A-Z
Most common cardiac diseases
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Cardiogenetic disorders
- Cardiomegaly
- Cardiomyopathy
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Chronic rheumatic heart diseases
- Congenital heart defects
- Heart neoplasia
- Ischemic heart diseases
- Pericardial disorders
- Syndromes affecting the heart
- Valvular heart disease
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
A[edit source]
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
- Acute decompensated heart failure
- Arteriosclerotic heart disease
- Athletic heart syndrome
- Atrial flutter
- Atrioventricular fistula
- Cardiovascular disease in Australia
- Autoimmune heart disease
B[edit source]
C[edit source]
- Ebb Cade
- Cardiac allograft vasculopathy
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Cardiac asthma
- Cardiac tamponade
- Cardiogenic shock
- Cardiogeriatrics
- Cardiorenal syndrome
- Cardiotoxicity
- Carditis
- Coronary artery aneurysm
- Coronary artery anomaly
- Coronary artery disease
- Spontaneous coronary artery dissection
- Coronary artery ectasia
- Coronary occlusion
- Coronary steal
- Coronary thrombosis
- Coronary vasospasm
- Cœur en sabot
- Coxsackievirus-induced cardiomyopathy
D[edit source]
E[edit source]
H[edit source]
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- Heart to Heart (1949 film)
- High-output heart failure
- Hyperdynamic precordium
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
I[edit source]
- Idiopathic giant-cell myocarditis
- Interventricular dyssynchrony
- Intraventricular dyssynchrony
- Isolated atrial amyloidosis
K[edit source]
L[edit source]
M[edit source]
- Mydicar
- Myocardial bridge
- Myocardial disarray
- Myocardial rupture
- Myocardial scarring
- Myocardial stunning
- Myocarditis
N[edit source]
O[edit source]
P[edit source]
- Papillary fibroelastoma
- Pathophysiology of heart failure
- Postpericardiotomy syndrome
- Pulmonary vein stenosis
R[edit source]
S[edit source]
- Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease
- SCAR-Fc
- Shone's syndrome
- Strain pattern
- Subacute bacterial endocarditis
- Sudden cardiac death of athletes
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
T[edit source]
V[edit source]
W[edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD

