The Lumbosacral Plexus
Anatomy > Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body > IX. Neurology > 6d. The Lumbosacral Plexus
Henry Gray (1821–1865). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918.
The Lumbosacral Plexus[edit | edit source]
(Plexus Lumbosacralis)
The anterior divisions of the lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal nerves form the lumbosacral plexus, the first lumbar nerve being frequently joined by a branch from the twelfth thoracic.
For descriptive purposes this plexus is usually divided into three parts—the lumbar, sacral and pudendal plexuses
The Lumbar Nerves (Nn. Lumbales)[edit | edit source]
The anterior divisions of the lumbar nerves (rami anteriores) increase in size from above downward. They are joined, near their origins, by gray rami communicantes from the lumbar ganglia of the sympathetic trunk.
These rami consist of long, slender branches which accompany the lumbar arteries around the sides of the vertebral bodies, beneath the Psoas major. Their arrangement is somewhat irregular: one ganglion may give rami to two lumbar nerves, or one lumbar nerve may receive rami from two ganglia.
The first and second, and sometimes the third and fourth lumbar nerves are each connected with the lumbar part of the sympathetic trunk by a white ramus communicans The nerves pass obliquely outward behind the Psoas major, or between its fasciculi, distributing filaments to it and the Quadratus lumborum. The first three and the greater part of the fourth are connected together in this situation by anastomotic loops, and form the lumbar plexus The smaller part of the fourth joins with the fifth to form the lumbosacral trunk which assists in the formation of the sacral plexus. The fourth nerve is named the nervus furcalis from the fact that it is subdivided between the two plexuses.
The Lumbar Plexus (plexus lumbalis) [edit | edit source]
(Figs. 822, 823, 824)The lumbar plexus is formed by the loops of communication between the anterior divisions of the first three and the greater part of the fourth lumbar nerves; the first lumbar often receives a branch from the last thoracic nerve. It is situated in the posterior part of the Psoas major, in front of the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae.
The mode in which the plexus is arranged varies in different subjects. It differs from the brachial plexus in not forming an intricate interlacement, but the several nerves of distribution arise from one or more of the spinal nerves, in the following manner: the first lumbar nerve, frequently supplemented by a twig from the last thoracic, splits into an upper and lower branch; the upper and larger branch divides into the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves; the lower and smaller branch unites with a branch of the second lumbar to form the genitofemoral nerve.
The remainder of the second nerve, and the third and fourth nerves, divide into ventral and dorsal divisions. The ventral division of the second unites with the ventral divisions of the third and fourth nerves to form the obturator nerve.
The dorsal divisions of the second and third nerves divide into two branches, a smaller branch from each uniting to form the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, and a larger branch from each joining with the dorsal division of the fourth nerve to form the femoral nerve. The accessory obturator, when it exists, is formed by the union of two small branches given off from the third and fourth nerves.
Branches[edit | edit source]
The branches of the lumbar plexus may therefore be arranged as follows: Iliohypogastric 1 L.
- Ilioinguinal 1 L.
- Genitofemoral 1, 2 L.
- Dorsal divisions.
- Lateral femoral cutaneous 2, 3 L.
- Femoral 2, 3, 4 L.
- Ventral divisions.
- Obturator 2, 3, 4 L.
- Accessory obturator 3, 4 L.
The Iliohypogastric Nerve (n. iliohypogastricus) arises from the first lumbar nerve. It emerges from the upper part of the lateral border of the Psoas major, and crosses obliquely in front of the Quadratus lumborum to the iliac crest. It then perforates the posterior part of the Transversus abdominis, near the crest of the ilium, and divides between that muscle and the Obliquus internus abdominis into a lateral and an anterior cutaneous branch
The lateral cutaneous branch (ramus cutaneus lateralis; iliac branch) pierces the Obliqui internus and externus immediately above the iliac crest, and is distributed to the skin of the gluteal region, behind the lateral cutaneous branch of the last thoracic nerve (Fig. 830); the size of this branch bears an inverse proportion to that of the lateral cutaneous branch of the last thoracic nerve.
The anterior cutaneous branch (ramus cutaneus anterior; hypogastric branch) (Fig. 825) continues onward between the Obliquus internus and Transversus. It then pierces the Obliquus internus, becomes cutaneous by perforating the aponeurosis of the Obliquus externus about 2.5 cm. above the subcutaneous inguinal ring, and is distributed to the skin of the hypogastric region.
The iliohypogastric nerve communicates with the last thoracic and ilioinguinal nerves.
The Ilioinguinal Nerve (n. ilioinguinalis), smaller than the preceding, arises with it from the first lumbar nerve. It emerges from the lateral border of the Psoas major just below the iliohypogastric, and, passing obliquely across the Quadratus lumborum and Iliacus, perforates the Transversus abdominis, near the anterior part of the iliac crest, and communicates with the iliohypogastric nerve between the Transversus and the Obliquus internus.
The nerve then pierces the Obliquus internus, distributing filaments to it, and, accompanying the spermatic cord through the subcutaneous inguinal ring, is distributed to the skin of the upper and medial part of the thigh, to the skin over the root of the penis and upper part of the scrotum in the male, and to the skin covering the mons pubis and labium majus in the female. The size of this nerve is in inverse proportion to that of the iliohypogastric. Occasionally it is very small, and ends by joining the iliohypogastric; in such cases, a branch from the iliohypogastric takes the place of the ilioinguinal, or the latter nerve may be altogether absent.
The Genitofemoral Nerve (n. genitofemoralis; genitocrural nerve) arises from the first and second lumbar nerves. It passes obliquely through the substance of the Psoas major, and emerges from its medial border, close to the vertebral column, opposite the fibrocartilage between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae; it then descends on the surface of the Psoas major, under cover of the peritoneum, and divides into the external spermatic and lumboinguinal nerves. Occasionally these two nerves emerge separately through the substance of the Psoas.
The external spermatic nerve (n. spermaticus externus; genital branch of genitofemoral) passes outward on the Psoas major, and pierces the fascia transversalis, or passes through the abdominal inguinal ring; it then descends behind the spermatic cord to the scrotum, supplies the Cremaster, and gives a few filaments to the skin of the scrotum. In the female, it accompanies the round ligament of the uterus, and is lost upon it.
The lumboinguinal nerve (n. lumboinguinalis; femoral or crural branch of genitofemoral) descends on the external iliac artery, sending a few filaments around it, and, passing beneath the inguinal ligament, enters the sheath of the femoral vessels, lying superficial and lateral to the femoral artery. It pierces the anterior layer of the sheath of the vessels and the fascia lata, and supplies the skin of the anterior surface of the upper part of the thigh (Fig. 825). On the front of the thigh it communicates with the anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve. A few filaments from the lumboinguinal nerve may be traced to the femoral artery.
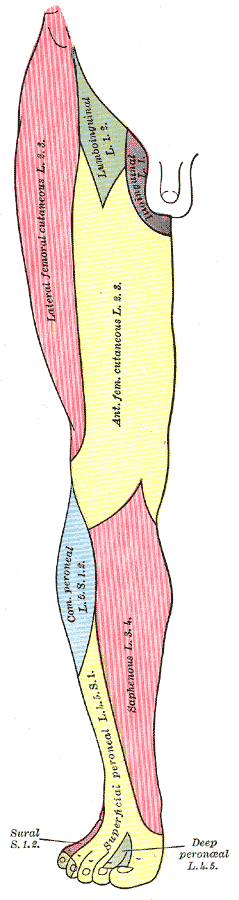
The Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve (n. cutaneus femoralis lateralis; external cutaneous nerve) arises from the dorsal divisions of the second and third lumbar nerves. It emerges from the lateral border of the Psoas major about its middle, and crosses the Iliacus obliquely, toward the anterior superior iliac spine. It then passes under the inguinal ligament and over the Sartorius muscle into the thigh, where it divides into two branches, and anterior and a posterior (Fig. 825).
The anterior branch becomes superficial about 10 cm. below the inguinal ligament, and divides into branches which are distributed to the skin of the anterior and lateral parts of the thigh, as far as the knee. The terminal filaments of this nerve frequently communicate with the anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve, and with the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve, forming with them the patellar plexus
The posterior branch pierces the fascia lata, and subdivides into filaments which pass backward across the lateral and posterior surfaces of the thigh, supplying the skin from the level of the greater trochanter to the middle of the thigh.
The Obturator Nerve (n. obturatorius) arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small. It descends through the fibers of the Psoas major, and emerges from its medial border near the brim of the pelvis; it then passes behind the common iliac vessels, and on the lateral side of the hypogastric vessels and ureter, which separate it from the ureter, and runs along the lateral wall of the lesser pelvis, above and in front of the obturator vessels, to the upper part of the obturator foramen. Here it enters the thigh, and divides into an anterior and a posterior branch, which are separated at first by some of the fibers of the Obturator externus, and lower down by the Adductor brevis.
The anterior branch (ramus anterior) (Fig. 827) leaves the pelvis in front of the Obturator externus and descends in front of the Adductor brevis, and behind the Pectineus and Adductor longus; at the lower border of the latter muscle it communicates with the anterior cutaneous and saphenous branches of the femoral nerve, forming a kind of plexus. It then descends upon the femoral artery, to which it is finally distributed. Near the obturator foramen the nerve gives off an articular branch to the hipjoint. Behind the Pectineus, it distributes branches to the Adductor longus and Gracilis, and usually to the Adductor brevis, and in rare cases to the Pectineus; it receives a communicating branch from the accessory obturator nerve when that nerve is present.
Occasionally the communicating branch to the anterior cutaneous and saphenous branches of the femoral is continued down, as a cutaneous branch, to the thigh and leg. When this is so, it emerges from beneath the lower border of the Adductor longus, descends along the posterior margin of the Sartorius to the medial side of the knee, where it pierces the deep fascia, communicates with the saphenous nerve, and is distributed to the skin of the tibial side of the leg as low down as its middle.
The posterior branch (ramus posterior) pierces the anterior part of the Obturator externus, and supplies this muscle; it then passes behind the Adductor brevis on the front of the Adductor magnus, where it divides into numerous muscular branches which are distributed to the Adductor magnus and the Adductor brevis when the latter does not receive a branch from the anterior division of the nerve. It usually gives off an articular filament to the knee-joint.
The articular branch for the knee-joint is sometimes absent; it either perforates the lower part of the Adductor magnus, or passes through the opening which transmits the femoral artery, and enters the popliteal fossa; it then descends upon the popliteal artery, as far as the back part of the knee-joint, where it perforates the oblique popliteal ligament, and is distributed to the synovial membrane. It gives filaments to the popliteal artery.
The Accessory Obturator Nerve (n. obturatorius accessorius) (Fig. 823) is present in about 29 per cent. of cases. It is of small size, and arises from the ventral divisions of the third and fourth lumbar nerves. It descends along the medial border of the Psoas major, crosses the superior ramus of the pubis, and passes under the Pectineus, where it divides into numerous branches. One of these supplies the Pectineus, penetrating its deep surface, another is distributed to the hip-joint; while a third communicates with the anterior branch of the obturator nerve. Occasionally the accessory obturator nerve is very small and is lost in the capsule of the hip-joint. When it is absent, the hip-joint receives two branches from the obturator nerve.
The Femoral Nerve (n. femoralis; anterior crural nerve) (Fig. 827), the largest branch of the lumbar plexus, arises from the dorsal divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves. It descends through the fibers of the Psoas major, emerging from the muscle at the lower part of its lateral border, and passes down between it and the Iliacus, behind the iliac fascia; it then runs beneath the inguinal ligament, into the thigh, and splits into an anterior and a posterior division. Under the inguinal ligament, it is separated from the femoral artery by a portion of the Psoas major.
Within the abdomen the femoral nerve gives off small branches to the Iliacus, and a branch which is distributed upon the upper part of the femoral artery; the latter branch may arise in the thigh.
In the thigh the anterior division of the femoral nerve gives off anterior cutaneous and muscular branches. The anterior cutaneous branches comprise the intermediate and medial cutaneous nerves (Fig. 825). 26
The intermediate cutaneous nerve (ramus cutaneus anterior; middle cutaneous nerve) pierces the fascia lata (and generally the Sartorius) about 7.5 cm. below the inguinal ligament, and divides into two branches which descend in immediate proximity along the forepart of the thigh, to supply the skin as low as the front of the knee. Here they communicate with the medial cutaneous nerve and the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous, to form the patellar plexus. In the upper part of the thigh the lateral branch of the intermediate cutaneous communicates with the lumboinguinal branch of the genitofemoral nerve.
The medial cutaneous nerve (ramus cutaneus anterior; internal cutaneous nerve) passes obliquely across the upper part of the sheath of the femoral artery, and divides in front, or at the medial side of that vessel, into two branches, an anterior and a posterior. The anterior branch runs downward on the Sartorius, perforates the fascia lata at the lower third of the thigh, and divides into two branches: one supplies the integument as low down as the medial side of the knee; the other crosses to the lateral side of the patella, communicating in its course with the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve. The posterior branch descends along the medial border of the Sartorius muscle to the knee, where it pierces the fascia lata, communicates with the saphenous nerve, and gives off several cutaneous branches. It then passes down to supply the integument of the medial side of the leg. Beneath the fascia lata, at the lower border of the Adductor longus, it joins to form a plexiform net-work (subsartorial plexus) with branches of the saphenous and obturator nerves. When the communicating branch from the obturator nerve is large and continued to the integument of the leg, the posterior branch of the medial cutaneous is small, and terminates in the plexus, occasionally giving off a few cutaneous filaments. The medial cutaneous nerve, before dividing, gives off a few filaments, which pierce the fascia lata, to supply the integument of the medial side of the thigh, accompanying the long saphenous vein. One of these filaments passes through the saphenous opening; a second becomes subcutaneous about the middle of the thigh; a third pierces the fascia at its lower third. '
MUSCULAR BRANCHES (rami musculares)
The nerve to the Pectineus arises immediately below the inguinal ligament, and passes behind the femoral sheath to enter the anterior surface of the muscle; it is often duplicated. The nerve to the Sartorius arises in common with the intermediate cutaneous. The posterior division of the femoral nerve gives off the saphenous nerve, and muscular and articular branches.
The Saphenous Nerve (n. saphenus; long or internal saphenous nerve) (Fig. 827) is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve. It approaches the femoral artery where this vessel passes beneath the Sartorius, and lies in front of it, behind the aponeurotic covering of the adductor canal, as far as the opening in the lower part of the Adductor magnus.
Here it quits the artery, and emerges from behind the lower edge of the aponeurotic covering of the canal; it descends vertically along the medial side of the knee behind the Sartorius, pierces the fascia lata, between the tendons of the Sartorius and Gracilis, and becomes subcutaneous. The nerve then passes along the tibial side of the leg, accompanied by the great saphenous vein, descends behind the medial border of the tibia, and, at the lower third of the leg, divides into two branches: one continues its course along the margin of the tibia, and ends at the ankle; the other passes in front of the ankle, and is distributed to the skin on the medial side of the foot, as far as the ball of the great toe, communicating with the medial branch of the superficial peroneal nerve.
BRANCHES
The saphenous nerve, about the middle of the thigh, gives off a branch which joins the subsartorial plexus. At the medial side of the knee it gives off a large infrapatellar branch which pierces the Sartorius and fascia lata, and is distributed to the skin in front of the patella.
This nerve communicates above the knee with the anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve; below the knee, with other branches of the saphenous; and, on the lateral side of the joint, with branches of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, forming a plexiform net-work, the plexus patellae The infrapatellar branch is occasionally small, and ends by joining the anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral, which supply its place in front of the knee.
Below the knee, the branches of the saphenous nerve are distributed to the skin of the front and medial side of the leg, communicating with the cutaneous branches of the femoral, or with filaments from the obturator nerve.
The muscular branches supply the four parts of the Quadriceps femoris. The branch to the Rectus femoris enters the upper part of the deep surface of the muscle, and supplies a filament to the hip-joint. The branch to the Vastus lateralis, of large size, accompanies the descending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex artery to the lower part of the muscle. It gives off an articular filament to the knee-joint.
The branch to the Vastus medialis descends lateral to the femoral vessels in company with the saphenous nerve. It enters the muscle about its middle, and gives off a filament, which can usually be traced downward, on the surface of the muscle, to the knee-joint. The branches to the Vastus intermedius, two or three in number, enter the anterior surface of the muscle about the middle of the thigh; a filament from one of these descends through the muscle to the Articularis genu and the knee-joint. The articular branch to the hip-joint is derived from the nerve to the Rectus femoris.
The articular branches to the knee-joint are three in number. One, a long slender filament, is derived from the nerve to the Vastus lateralis; it penetrates the capsule of the joint on its anterior aspect. Another, derived from the nerve to the Vastus medialis, can usually be traced downward on the surface of this muscle to near the joint; it then penetrates the muscular fibers, and accompanies the articular branch of the highest genicular artery, pierces the medial side of the articular capsule, and supplies the synovial membrane. The third branch is derived from the nerve to the Vastus intermedius.
Note 135 In most cases the fourth lumbar is the nervus furcalis but this arrangement is frequently departed from. The third is occasionally the lowest nerve which enters the lumbar plexus, giving at the same time some fibers to the sacral plexus, and thus forming the nervus furcalis; or both the third and fourth may be furcal nerves. When this occurs, the plexus is termed high or prefixed More frequently the fifth nerve is divided between the lumbar and sacral plexuses, and constitutes the nervus furcalis; and when this takes place, the plexus is distinguished as a low or postfixed plexus. These variations necessarily produce corresponding modifications in the sacral plexus.
Note 136 Bardeen, Amer. Jour. Anat., 1907, vol. vi.
Additional Images[edit | edit source]
| Nerves of the lumbosacral plexus | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
This article is a neuroscience stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
External links[edit | edit source]
- Atlas image: abdo_wall72 at the University of Michigan Health System - "Lumbosacral Plexus"
Gray's Anatomy[edit source]
- Gray's Anatomy Contents
- Gray's Anatomy Subject Index
- About Classic Gray's Anatomy
- Glossary of anatomy terms
Anatomy atlases (external)[edit source]
[1] - Anatomy Atlases
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
| Human systems and organs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Deepika vegiraju, Prab R. Tumpati, MD