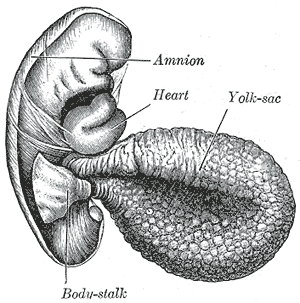
The Yolk-sac
Henry Gray (1821–1865). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918.
The Yolk-sac[edit | edit source]
The yolk-sac (Figs. 22 and 23) is situated on the ventral aspect of the embryo; it is lined by entoderm, outside of which is a layer of mesoderm. It is filled with fluid, the vitelline fluid which possibly may be utilized for the nourishment of the embryo during the earlier stages of its existence.
Blood is conveyed to the wall of the sac by the primitive aorta, and after circulating through a wide-meshed capillary plexus, is returned by the vitelline veins to the tubular heart of the embryo.
This constitutes the vitelline circulation and by means of it nutritive material is absorbed from the yolk-sac and conveyed to the embryo. At the end of the fourth week the yolk-sac presents the appearance of a small pear-shaped vesicle (umbilical vesicle) opening into the digestive tube by a long narrow tube, the vitelline duct .
The vesicle can be seen in the after-birth as a small, somewhat oval-shaped body whose diameter varies from 1 mm. to 5 mm, it is situated between the amnion and the chorion and may lie on or at a varying distance from the placenta.
As a rule the duct undergoes complete obliteration during the seventh week, but in about three per cent. of cases its proximal part persists as a diverticulum from the small intestine, Meckel’s diverticulum which is situated about three or four feet above the ileocolic junction, and may be attached by a fibrous cord to the abdominal wall at the umbilicus.
Sometimes a narrowing of the lumen of the ileum is seen opposite the site of attachment of the duct.
Cord blood[edit | edit source]
Recently, it has been discovered that the blood within the umbilical cord, known as cord blood, is a rich and readily available source of primitive,Cellular differentiation|undifferentiated stem cells (i.e. CD34+ and CD38-). These cord blood cells can be used for bone marrow transplant.
Some parents have opted to have this blood harvested upon the baby's birth, and frozen for long-term storage at a cord blood bank should the child ever require the cord blood stem cells (for example, to replace bone marrow destroyed when treating leukemia). This practice is somewhat controversial.
Additional images[edit | edit source]
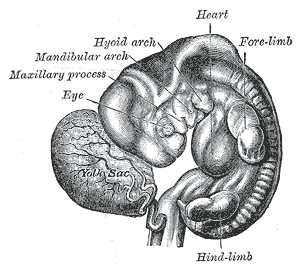
Human embryo about fifteen days old. Brain and heart represented from right side. Digestive tube and yolk sac in median section.
References[edit | edit source]
| Development of the reproductive system | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Membranes of the fetus and embryo | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gray's Anatomy[edit source]
- Gray's Anatomy Contents
- Gray's Anatomy Subject Index
- About Classic Gray's Anatomy
- Glossary of anatomy terms
Anatomy atlases (external)[edit source]
[1] - Anatomy Atlases
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
| Human systems and organs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Deepika vegiraju, Prab R. Tumpati, MD