Scrub typhus
(Redirected from Tsutsugamushi)
A bacterial disease transmitted by larval mites and widespread in Asia.
Other names[edit | edit source]
Scrub typhus, also known as bush typhus, is a disease caused by a bacteria called Orientia tsutsugamushi. Scrub typhus is spread to people through bites of infected chiggers (larval mites). The most common symptoms of scrub typhus include fever, headache, body aches, and sometimes rash. Most cases of scrub typhus occur in rural areas of Southeast Asia, Indonesia, China, Japan, India, and northern Australia. Anyone living in or traveling to areas where scrub typhus is found could get infected.
Signs and Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of scrub typhus usually begin within 10 days of being bitten. Signs and symptoms may include:
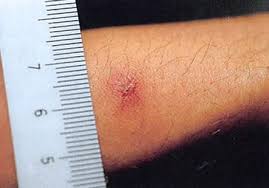
- Scrub typhus eschar
- Fever and chills
- Headache
- Body aches and muscle pain
- A dark, scab-like region at the site of the chigger bite (also known as eschar)
- Mental changes, ranging from confusion to coma
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Rash
People with severe illness may develop organ failure and bleeding, which can be fatal if left untreated.
Diagnosis and Testing[edit | edit source]
The symptoms of scrub typhus are similar to symptoms of many other diseases. See your health care provider if you develop the symptoms listed above after spending time in areas where scrub typhus is found. If you have recently traveled, tell your health care provider where and when you traveled. Your health care provider may order blood tests to look for scrub typhus or other diseases. Laboratory testing and reporting of results can take several weeks, so your health care provider may start treatment before results are available.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Scrub typhus should be treated with the antibiotic doxycycline. Doxycycline can be used in persons of any age. Antibiotics are most effective if given soon after symptoms begin. People who are treated early with doxycycline usually recover quickly.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
- Adult and larval chiggers
- No vaccine is available to prevent scrub typhus.
- Reduce your risk of getting scrub typhus by avoiding contact with infected chiggers.
- When traveling to areas where scrub typhus is common, avoid areas with lots of vegetation and brush where chiggers may be found.
- If you will be spending time outdoors:
- Use Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)-registered insect repellent containing DEET or other active ingredients registered for use against chiggers, on exposed skin and clothing.
Other measures[edit | edit source]
- Always follow product instructions.
- Reapply insect repellent as directed.
- Do not spray repellent on the skin under clothing.
- If you are also using sunscreen, apply sunscreen before applying insect repellent.
- If you have a baby or child:
- Dress your child in clothing that covers arms and legs, or cover crib, stroller, and baby carrier with mosquito netting.
- Do not apply insect repellent onto a child’s hands, eyes, or mouth or on cuts or irritated skin.
- Adults: Spray insect repellent onto your hands and then apply to child’s face.
- Treat clothing and gear with permethrin or purchase permethrin-treated items.
- Permethrin kills chiggers and can be used to treat boots, clothing, and camping gear.
- o Treated clothing remains protective after multiple washings. See product information to learn how long the protection will last.
- o If treating items yourself, follow the product instructions carefully.
- o Do NOT use permethrin products directly on skin. They are intended to treat clothing.
See also[edit | edit source]
| Scrub typhus Resources | |
|---|---|
|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD