Aqueductal stenosis
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Aqueductal stenosis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, nausea, vomiting, vision problems, balance issues |
| Complications | Hydrocephalus, increased intracranial pressure |
| Onset | Can occur at any age |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Congenital malformation, tumor, infection, hemorrhage |
| Risks | Genetic factors, infections during pregnancy |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT scan, neurological examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Arnold-Chiari malformation, Dandy-Walker syndrome, tumor |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Ventriculoperitoneal shunt, endoscopic third ventriculostomy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on cause and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Aqueductal Stenosis
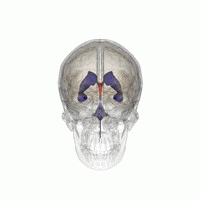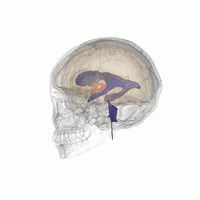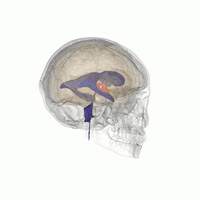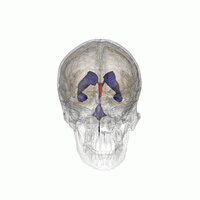
Aqueductal stenosis is a condition characterized by the narrowing of the cerebral aqueduct, also known as the aqueduct of Sylvius, which is a channel that connects the third and fourth ventricles in the brain. This narrowing can lead to the obstruction of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow, resulting in a condition known as hydrocephalus.
Anatomy and Physiology
The cerebral aqueduct is a slender canal located in the midbrain, part of the brainstem. It is approximately 1.5 mm in diameter and serves as a conduit for CSF to flow from the third ventricle, located in the diencephalon, to the fourth ventricle, situated between the pons and the cerebellum. The proper functioning of the cerebral aqueduct is crucial for maintaining normal CSF circulation and intracranial pressure.
Pathophysiology
Aqueductal stenosis can be congenital or acquired. Congenital aqueductal stenosis is often due to developmental anomalies, such as aqueductal webs or gliosis. Acquired causes include tumors, infections, or hemorrhage that lead to scarring and narrowing of the aqueduct. The obstruction of CSF flow results in increased pressure in the ventricles proximal to the obstruction, leading to ventricular dilation and hydrocephalus. This can cause symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, and papilledema. In infants, it may lead to an increase in head size and bulging fontanelles.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of aqueductal stenosis is typically made using neuroimaging techniques. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred method as it provides detailed images of the brain's ventricular system and can identify the site and cause of the obstruction. Computed tomography (CT) scans may also be used, particularly in emergency settings.
Treatment
The primary treatment for aqueductal stenosis is surgical intervention to restore normal CSF flow. The most common procedure is the placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt, which diverts excess CSF from the ventricles to the peritoneal cavity, where it can be absorbed. Another surgical option is endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV), which creates an opening in the floor of the third ventricle to allow CSF to bypass the obstruction.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with aqueductal stenosis depends on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the success of the treatment. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for preventing long-term complications such as cognitive impairment and motor deficits.
See also
- Hydrocephalus
- Cerebrospinal fluid
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunt
- Endoscopic third ventriculostomy
- Brainstem
WikiMD neurology
| Neurology |
| Neurological diseases and disorders
Cerebrovascular diseases | Chronic fatigue syndrome | Congenital disorders of nervous system | Demyelinating diseases of CNS Epilepsy | Extrapyramidal and movement disorders | Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system Motion sickness | Myoneural junction and neuromuscular diseases | Nervous system neoplasia Sleep disorders | Neurocutaneous conditions | Neurodegenerative disorders | Neurodevelopmental disorders |
External links
- Comprehensive information from the National Institute of health.
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD