Hernia
(Redirected from Herniation)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hernia | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Rupture |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling |
| Complications | Strangulation, bowel obstruction |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Increased intra-abdominal pressure, weakness of the abdominal wall |
| Risks | Obesity, pregnancy, heavy lifting, chronic cough |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging |
| Differential diagnosis | Hydrocele, lymphadenopathy, testicular torsion |
| Prevention | Weight management, avoiding heavy lifting |
| Treatment | Surgery (herniorrhaphy, hernia repair), watchful waiting |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Hernias: Types, Causes, and Treatments[edit | edit source]
A hernia is the bulging of an internal organ through a weak area or tear in the muscle or other tissue that holds it in place. Most hernias occur in the abdomen and can cause extreme pain. They may be caused by muscle weakness or straining due to heavy lifting. Treatment typically involves surgery to remove the hernia. There are several different types of hernias, including congenital diaphragmatic hernia, hiatal hernia, incisional hernia, inguinal hernia, and umbilical hernia.
Types of Hernias[edit | edit source]
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia[edit | edit source]
A congenital diaphragmatic hernia is a birth defect where the diaphragm fails to close properly during fetal development. This results in the abdominal organs pushing into the chest cavity, which can impair lung development and cause breathing difficulties after birth. Surgery is necessary to repair the defect.
Hiatal Hernia[edit | edit source]
A hiatal hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach pushes through a small opening in the diaphragm (the hiatus) and moves up into the chest cavity. There are two main types of hiatal hernias: sliding hiatal hernias, which are more common, and paraesophageal hernias, which are less common but more dangerous. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medication, and, in severe cases, surgery.
Incisional Hernia[edit | edit source]
An incisional hernia develops at the site of a previous surgical incision in the abdominal wall. This type of hernia can occur due to the weakening of the muscle tissue around the incision, leading to a protrusion of the underlying organs or tissue. Treatment generally involves surgical repair, which may include the use of mesh to reinforce the weakened area.
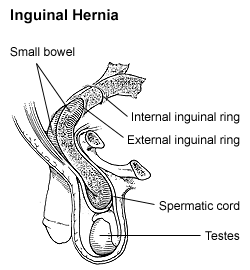
Inguinal Hernia[edit | edit source]
An inguinal hernia is the most common type of hernia and occurs in the groin area. It results from a weakness in the lower abdominal wall, allowing a part of the intestine or fatty tissue to push through the inguinal canal. Inguinal hernias can be further classified as direct or indirect. Treatment usually involves surgical repair, either through open surgery or laparoscopic (minimally invasive) techniques.
Umbilical Hernia[edit | edit source]
An umbilical hernia occurs when a part of the intestine or fatty tissue protrudes through a weak spot near the belly button (umbilicus). While it is more common in infants, it can also occur in adults. Small umbilical hernias may resolve on their own, but larger ones usually require surgical repair.
Causes of Hernias[edit | edit source]
Hernias are generally caused by a combination of muscle weakness and strain. Factors that contribute to hernia development include:
- Congenital defects, such as weak abdominal muscles or an improperly formed diaphragm
- Aging, which can lead to muscle weakness
- Chronic coughing or sneezing
- Obesity, which can put pressure on the abdominal muscles
- Heavy lifting or strenuous physical activity
- Pregnancy, particularly multiple pregnancies
- Previous abdominal surgery, which may weaken the muscles or tissues
- Constipation, which can cause straining during bowel movements
- Smoking, as it can weaken connective tissues
Symptoms of Hernias[edit | edit source]
Hernia symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity. Common symptoms include:
- A visible bulge or lump in the affected area, particularly when coughing, lifting, or straining
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area, which may worsen with activity
- A feeling of heaviness or pressure in the affected area
- In some cases, nausea, vomiting, or difficulty passing bowel movements, particularly if the hernia becomes incarcerated or strangulated
Diagnosis of Hernias[edit | edit source]
Hernias are typically diagnosed through a physical examination by a healthcare professional. The doctor may ask the patient to cough, bend, or strain to observe the hernia's appearance. In some cases, imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or CT scans, may be required to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of the hernia.
Treatment of Hernias[edit | edit source]
Treatment for hernias depends on the type, size, and severity of the hernia, as well as the patient's overall health. Treatment options include:
- Watchful waiting: In some cases, particularly for small, asymptomatic hernias, a doctor may recommend monitoring the hernia for any changes or complications.
- Lifestyle changes: For certain types of hernias, such as hiatal hernias, making lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms. These changes may include weight loss, avoiding heavy lifting, and dietary adjustments to reduce acid reflux.
- * Medications: For hiatal hernias, over-the-counter antacids, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors may be recommended to control acid reflux symptoms.
- * Surgery: Surgical intervention is the primary treatment for most hernias. Surgery can be performed using open or laparoscopic techniques, depending on the specific situation. The procedure typically involves returning the protruding organ or tissue to its proper place and repairing the defect in the muscle or tissue, often with the use of a mesh to reinforce the area and prevent recurrence.
Complications of Hernias[edit | edit source]
If left untreated, hernias can lead to complications, such as:
- Incarceration: A hernia becomes incarcerated when the protruding tissue becomes trapped, resulting in an inability to return it to its proper position. This may cause pain and discomfort, and in some cases, bowel obstruction.
- Strangulation: Strangulation occurs when the blood supply to the incarcerated hernia is compromised, leading to tissue death. This is a medical emergency requiring immediate surgical intervention to prevent life-threatening complications.
Prevention of Hernias[edit | edit source]
While not all hernias can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices may help reduce the risk of developing a hernia:
- Maintain a healthy body weight
- Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen abdominal muscles
- Avoid heavy lifting or learn proper
- lifting techniques to reduce strain on abdominal muscles
- Quit smoking, as it can weaken connective tissues
- Treat and manage chronic coughing or sneezing
- Avoid constipation by incorporating a high-fiber diet and staying well-hydrated
Summary[edit | edit source]
The bulging of an internal organ through a weak area or tear in the muscle or other tissue that holds it in place. Most hernias occur in the abdomen. Hernias may be caused by muscle weakness or straining due to heavy lifting. Hernias can cause extreme pain. Treatment is surgery to remove the hernia. There are several different types of hernias, including: Congenital diaphragmatic hernia-a birth defect that needs surgery. Hiatal hernia-small opening in the diaphragm that allows the upper part of the stomach to move up into the chest. Incisional hernia-due to a scar. Inguinal hernia-This is the the most common type and occurs in the groin. Umbilical hernia-occurs around the belly button.
What causes a hernia?
A hernia is caused by a combination of muscle weakness and strain. Factors contributing to hernia development include congenital defects, aging, chronic coughing or sneezing, obesity, heavy lifting, pregnancy, previous abdominal surgery, constipation, and smoking.
What are the different types of hernias?
There are several types of hernias, including congenital diaphragmatic hernia, hiatal hernia, incisional hernia, inguinal hernia, and umbilical hernia.
What should you not do with a hernia?
With a hernia, you should avoid heavy lifting, strenuous activities, smoking, and constipation, as these can worsen symptoms or increase the risk of complications.
How do they repair a hiatal hernia?
A hiatal hernia is repaired through surgery, which can be performed using open or laparoscopic techniques. The surgeon pulls the stomach back into the abdomen, tightens the diaphragm opening, and may use a mesh to reinforce the area.
What foods should I avoid with a hernia?
Foods to avoid with a hernia, particularly a hiatal hernia, include acidic or spicy foods, fatty or fried foods, alcohol, and carbonated beverages, as they can aggravate symptoms.
Can you fix a hernia without surgery?
In some cases, small hernias can be managed with lifestyle changes and conservative treatments, but surgery is typically the most effective and definitive treatment for most hernias.
What aggravates a hernia?
Heavy lifting, strenuous activities, smoking, constipation, and obesity can aggravate a hernia by increasing pressure on the abdominal muscles and worsening symptoms.
Is it OK to live with a hernia?
It may be acceptable to live with a small, asymptomatic hernia under a doctor's supervision. However, untreated hernias can lead to complications, so it is essential to monitor the condition and seek treatment if symptoms worsen or complications arise.
How many hours is hiatal hernia surgery?
Hiatal hernia surgery typically takes 2-4 hours, depending on the complexity of the case and the surgical technique used.
What is the downside of hiatal hernia surgery?
Potential downsides of hiatal hernia surgery include risks associated with anesthesia, infection, bleeding, injury to surrounding organs, and recurrence of the hernia.
Is it worth getting hiatal hernia surgery?
Hiatal hernia surgery may be worth considering if conservative treatments have not effectively managed symptoms, or if the hernia is causing significant discomfort or complications.
Is banana good for hernia?
Bananas are a good food choice for those with a hernia, as they are easy to digest and can help counteract stomach acidity in cases of hiatal hernia.
Can you eat salad with a hernia?
Yes, you can eat salad with a hernia. Fresh vegetables and fruits are an integral part of any healthy diet.
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
| Health science - Medicine - Gastroenterology - edit |
|---|
| Diseases of the esophagus - stomach |
| Halitosis | Nausea | Vomiting | GERD | Achalasia | Esophageal cancer | Esophageal varices | Peptic ulcer | Abdominal pain | Stomach cancer | Functional dyspepsia | Gastroparesis |
| Diseases of the liver - pancreas - gallbladder - biliary tree |
| Hepatitis | Cirrhosis | NASH | PBC | PSC | Budd-Chiari | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Acute pancreatitis | Chronic pancreatitis | Pancreatic cancer | Gallstones | Cholecystitis |
| Diseases of the small intestine |
| Peptic ulcer | Intussusception | Malabsorption (e.g. Coeliac, lactose intolerance, fructose malabsorption, Whipple's) | Lymphoma |
| Diseases of the colon |
| Diarrhea | Appendicitis | Diverticulitis | Diverticulosis | IBD (Crohn's, Ulcerative colitis) | IBS | Constipation | Colorectal cancer | Hirschsprung's | Pseudomembranous colitis |
| Congenital diaphragm and abdominal wall defects, abdominopelvic cavity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD





