Myocardial infarction
(Redirected from Acute myocardial infarction)
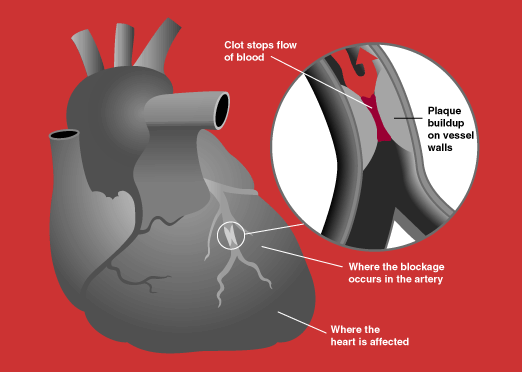
Myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. The blockage is most often a result of atherosclerosis, a condition in which fatty deposits (plaques) build up in the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. An MI can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The most common symptoms of myocardial infarction include:
- Chest pain or discomfort, often described as a heavy pressure, squeezing, or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sweating
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue
Symptoms can vary between individuals and may be milder or more severe. In some cases, individuals may experience a "silent" myocardial infarction, which presents with minimal or no symptoms.
Causes[edit | edit source]
The primary cause of myocardial infarction is atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fatty plaques within the coronary arteries. Plaques can rupture, leading to the formation of a blood clot, which blocks blood flow to the heart muscle. Other less common causes of MI include coronary artery spasm and coronary artery dissection.
Risk factors[edit | edit source]
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a myocardial infarction:
- Smoking
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Family history of heart disease
- Age (older individuals are at higher risk)
- Gender (men are at higher risk than women)
- Chronic kidney disease
- Stress
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction typically involves:
Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the electrical activity of the heart and can identify areas of damage or abnormal rhythms. Blood tests: Troponin and CK-MB are proteins released into the bloodstream when the heart muscle is damaged. Elevated levels of these proteins can indicate a myocardial infarction. Cardiac imaging: Echocardiography, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or nuclear scans can help visualize the heart and assess the extent of damage.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for myocardial infarction aims to restore blood flow to the heart and minimize damage to the heart muscle. Treatment options include:
- Aspirin: Chewable aspirin can help thin the blood and prevent further clot formation. Aspirin should be taken as soon as possible after the onset of symptoms.
- Nitroglycerin: This medication can help alleviate chest pain by relaxing the coronary arteries and improving blood flow to the heart.
- Beta blockers: These drugs reduce the workload on the heart and lower blood pressure, minimizing the risk of further heart damage.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: ACE inhibitors help relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure, improving blood flow and reducing the strain on the heart.
- Angioplasty and stent placement: In this procedure, a catheter is threaded through the blocked artery, and a balloon is inflated to compress the plaque against the arterial walls. A stent is then placed to keep the artery open.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): In more severe cases, a CABG surgery may be performed to reroute blood flow around the blocked artery using a graft, usually taken from a vein or artery in the leg, chest, or arm.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Preventing myocardial infarction involves managing risk factors and maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle. Some preventive measures include:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats
- Regular exercise (at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week)
- Avoiding tobacco use and limiting alcohol consumption
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises
- Regularly monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for myocardial infarction depends on several factors, including the severity of the infarction, the extent of heart damage, and the effectiveness of treatment. Timely intervention and adherence to recommended lifestyle changes can greatly improve the prognosis for many individuals. However, some patients may develop complications, such as heart failure, arrhythmias, or cardiogenic shock, which can be life-threatening.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Myocardial infarction is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The incidence of MI varies across populations and is influenced by age, gender, and socioeconomic factors. Early diagnosis and improved treatment strategies have contributed to a decline in mortality rates in recent decades, but the overall burden of MI remains high.
See also[edit | edit source]
| Cardiovascular disease (heart) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Disorders of blood flow | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD