Pancreas
(Redirected from Body of pancreas)
The pancreas is a long, soft organ that lies in the abdomen that plays an important role in both the endocrine system and digestion.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The pancreas lies transversely along the posterior abdominal wall, posterior to the stomach, and extends from the region of the duodenum to the spleen.
Etiology[edit | edit source]
The word pancreas is from the Greek πᾶν (pân, “all”) & κρέας (kréas, “flesh”).
Structure[edit | edit source]
The pancreas is an intra-abdominal organ that in humans lies in the abdomen, stretching from behind the stomach to the left upper abdomen near the spleen.
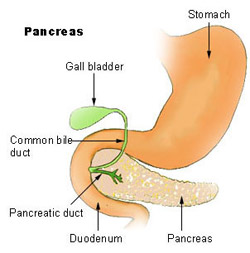
Parts of pancreas[edit | edit source]
Anatomically, the pancreas is divided into a head, neck, body, and tail. The pancreas stretches from the inner curvature of the duodenum, where the head surrounds two blood vessels: the superior mesenteric artery, and vein.
Blood supply[edit | edit source]
The pancreas has a rich blood supply, with vessels originating as branches of both the coeliac artery and superior mesenteric artery.
The body and neck of the pancreas drain into the splenic vein, which sits behind the pancreas and the head drains into, and wraps around, the superior mesenteric and portal veins, via the pancreaticoduodenal veins.
The lymphatic vessels of the body and tail drain into splenic lymph nodes, and eventually into lymph nodes that lie in front of the aorta, between the coeliac and superior mesenteric arteries. The lymphatic vessels of the head and neck drain into intermediate lymphatic vessels around the pancreaticoduodenal, mesenteric and hepatic arteries, and from there into the lymph nodes that lie in front of the aorta.
Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. Because of its role in the regulation of blood sugar, the pancreas is also a key organ in diabetes mellitus. Pancreatic cancer can arise following chronic pancreatitis or due to other reasons, and carries a very poor prognosis, as it is often identified when it has spread to other areas of the body.
Function[edit | edit source]
Pancreas is one of very few organs in the body that has both endocrine and exocrine functions.
Exocrine fuction[edit | edit source]
The pancreas has an exocrine portion that secretes digestive enzymes that are carried through a duct called pancreatic duct to the duodenum.
Endocrine function[edit | edit source]
The endocrine portion consists of the pancreatic islets, which secrete glucagons and insulin.
- The alpha cells in the pancreatic islets secrete the hormone glucagon in response to a low concentration of glucose in the blood.
- Beta cells in the pancreatic islets, called islets of Langerhans, secrete the hormone insulin in response to a high concentration of glucose in the blood.
Pancreatic disorders[edit | edit source]
| Anatomy of the liver, pancreas and biliary tree | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD