Echinococcosis
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Echinococcosis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, cough, fever |
| Complications | Cyst rupture, anaphylaxis, biliary obstruction |
| Onset | Months to years after exposure |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Infection by Echinococcus species |
| Risks | Contact with infected animals, sheep farming, dog ownership |
| Diagnosis | Imaging (e.g., ultrasound, CT scan), serology |
| Differential diagnosis | Liver abscess, tumor, hydatidiform mole |
| Prevention | Deworming dogs, proper handling of animals, hygiene |
| Treatment | Surgery, antiparasitic medication (e.g., albendazole) |
| Medication | Albendazole, mebendazole |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on location and size of cysts |
| Frequency | Common in sheep farming regions |
| Deaths | N/A |
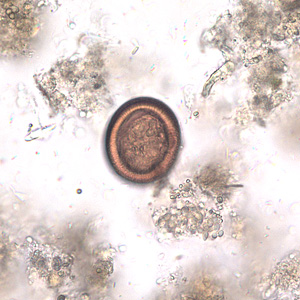
A parasitic infection caused by tapeworm larvae of echinococcus. It affects livestock and humans.
It is characterized by the formation of hydatid cysts mainly in the liver, lungs, spleen, and kidneys.
Rupture of the cysts may lead to shock.
Types[edit | edit source]
Echinococcosis is classified as either cystic echinococcosis or alveolar echinococcosis. Cystic echinocccosis (CE), also known as hydatid disease, is caused by infection with the larval stage of Echinococcus granulosus, a ~2-7 millimeter long tapeworm found in dogs (definitive host) and sheep, cattle, goats, and pigs (intermediate hosts).
- Although most infections in humans are asymptomatic, CE causes harmful, slowly enlarging cysts in the liver, lungs, and other organs that often grow unnoticed and neglected for years.
Alveolar echinococcosis (AE) disease is caused by infection with the larval stage of Echinococcus multilocularis, a ~1-4 millimeter long tapeworm found in foxes, coyotes, and dogs (definitive hosts).
- Small rodents are intermediate hosts for E.multilocularis.
- Although cases of AE in animals in endemic areas are relatively common, human cases are rare.
- AE poses a much greater health threat to people than CE, causing parasitic tumors that can form in the liver, lungs, brain, and other organs.
- If left untreated, AE can be fatal.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
- Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is caused by infection with the larval stage of Echinococcus granulosus.
- CE is found in Africa, Europe, Asia, the Middle East, Central and South America, and in rare cases, North America.
- The parasite is transmitted to dogs when they ingest the organs of other animals that contain hydatid cysts.
- The cysts develop into adult tapeworms in the dog.
- Infected dogs shed tapeworm eggs in their feces which contaminate the ground.
- Sheep, cattle, goats, and pigs ingest tapeworm eggs in the contaminated ground; once ingested, the eggs hatch and develop into cysts in the internal organs.
Transmission[edit | edit source]
- The most common mode of transmission to humans is by the accidental consumption of soil, water, or food that has been contaminated by the fecal matter of an infected dog.
- Echinococcus eggs that have been deposited in soil can stay viable for up to a year.
- The disease is most commonly found in people involved in raising sheep, as a result of the sheep’s role as an intermediate host of the parasite and the presence of working dogs that are allowed to eat the offal of infected sheep.
- Alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is caused by infection with the larval stage of Echinococcus multilocularis.
- AE is found across the globe and is especially prevalent in the northern latitudes of Europe, Asia, and North America.
- The adult tapeworm is normally found in foxes, coyotes, and dogs.
- Infection with the larval stages is transmitted to people through ingestion of food or water contaminated with tapeworm eggs.
Cause[edit | edit source]
- Human echinococcosis (hydatidosis, or hydatid disease) is caused by the larval stages of cestodes (tapeworms) of the genus Echinococcus.
- Echinococcus granulosus (sensu lato) causes cystic echinococcosis and is the form most frequently encountered.
- Another species, E.multilocularis, causes alveolar echinococcosis, and is becoming increasingly more common.
- Two exclusively New World species, E.vogeli and E.oligarthrus, are associated with “Neotropical echinococcosis”; E.vogeli causes a polycystic form whereas E.oligarthrus causes the extremely rare unicystic form.
lifecycle[edit | edit source]
- The adult Echinococcus granulosus (sensu lato) (2—7 mm long) resides in the small intestine of the definitive host.
- Gravid proglottids release eggs that are passed in the feces, and are immediately infectious.
- After ingestion by a suitable intermediate host, eggs hatch in the small intestine and release six-hooked oncospheres that penetrate the intestinal wall and migrate through the circulatory system into various organs, especially the liver and lungs.
- In these organs, the oncosphere develops into a thick-walled hydatid cyst that enlarges gradually, producing protoscolices and daughter cysts that fill the cyst interior.
- The definitive host becomes infected by ingesting the cyst-containing organs of the infected intermediate host.
- After ingestion, the protoscolices evaginate, attach to the intestinal mucosa , and develop into adult stages in 32 to 80 days.
- Humans are aberrant intermediate hosts, and become infected by ingesting eggs .
- Oncospheres are released in the intestine , and hydatid cysts develop in a variety of organs.
- ==Diagnosis==
- The presence of a cyst-like mass in a person with a history of exposure to sheepdogs in an area where E.granulosus is endemic suggests a diagnosis of cystic echinococcosis.
- Imaging techniques, such as CT scans, ultrasonography, and MRIs, are used to detect cysts.
- After a cyst has been detected, serologic tests may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
- Alveolar echinococcosis is typically found in older people.
- Imaging techniques such as CT scans are used to visually confirm the parasitic vesicles and cyst-like structures and serologic tests can confirm the parasitic infection.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
- In the past, surgery was the only treatment for cystic echinococcal cysts.
- Chemotherapy, cyst puncture, and PAIR (percutaneous aspiration, injection of chemicals and reaspiration) have been used to replace surgery as effective treatments for cystic echinococcosis.
- However, surgery remains the most effective treatment to remove the cyst and can lead to a complete cure.
- Some cysts are not causing any symptoms and are inactive; those cysts often go away without any treatment.
- The treatment of alveolar echinococcosis is more difficult than cystic echinococcosis and usually requires radical surgery, long-term chemotherapy, or both.
Prevention & Control[edit | edit source]
- Cystic echinococcosis is controlled by preventing transmission of the parasite.
- Prevention measures include limiting the areas where dogs are allowed and preventing animals from consuming meat infected with cysts.
- Prevent dogs from feeding on the carcasses of infected sheep.
- Control stray dog populations.
- Restrict home slaughter of sheep and other livestock.
- Do not consume any food or water that may have been contaminated by fecal matter from dogs.
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water after handling dogs, and before handling food.
Washing hands[edit | edit source]
- Teach children the importance of washing hands to prevent infection.
- Alveolar echinococcosis can be prevented by avoiding contact with wild animals such as foxes, coyotes, and dogs and their fecal matter and by limiting the interactions between dogs and rodent populations.
- Do not allow dogs to feed on rodents and other wild animals.
- Avoid contact with wild animals such as foxes, coyotes and stray dogs.
- Do not encourage wild animals to come close to your home or keep them as pets.
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water after handling dogs or cats, and before handling food.
- Teach children the importance of washing hands to prevent infection.
| Parasitic disease caused by helminthiases | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Dogs | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD