Hallermann–Streiff syndrome
(Redirected from Hallermann's syndrome)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hallermann–Streiff syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Hallermann-Streiff-François syndrome, Oculomandibulofacial syndrome |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | Dwarfism, craniofacial dysmorphism, dental abnormalities, hypotrichosis, cataracts |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation (unknown specific gene) |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis |
| Differential diagnosis | Progeria, Crouzon syndrome, Apert syndrome |
| Prevention | None |
| Treatment | Symptomatic treatment, surgical intervention |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on severity of symptoms |
| Frequency | Rare, estimated <1 in 1,000,000 |
| Deaths | |
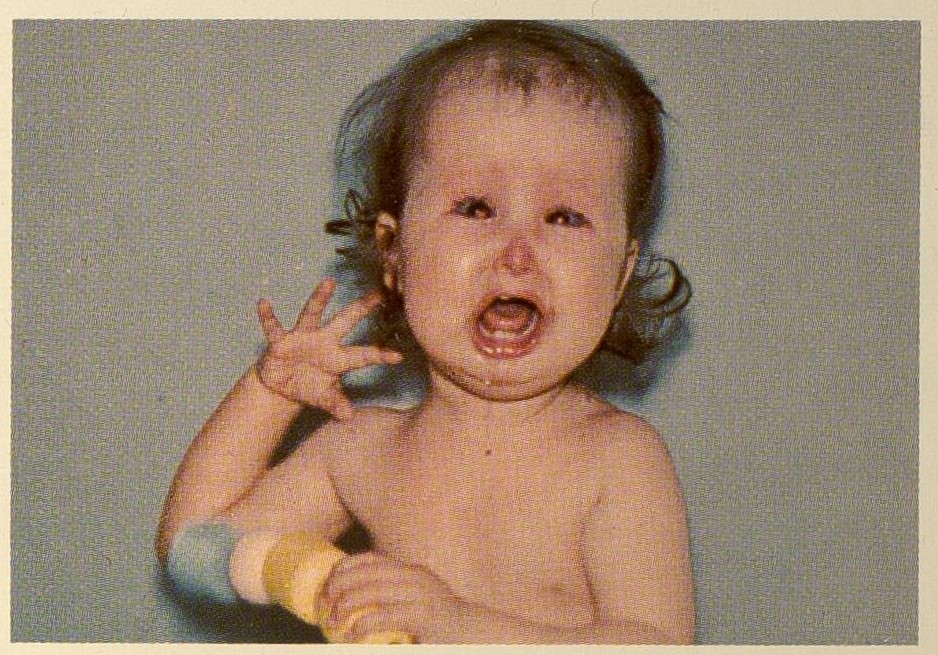
Hallermann–Streiff syndrome (HSS) is a rare congenital disorder characterized by distinctive craniofacial abnormalities, dental anomalies, and proportionate dwarfism. The syndrome is named after the German ophthalmologist Wilhelm Hallermann and the Swiss ophthalmologist Enrico Streiff, who first described the condition in the 20th century.
Clinical Features[edit | edit source]
Individuals with Hallermann–Streiff syndrome typically present with a combination of the following features:
- Craniofacial dysmorphisms: These include a small head (microcephaly), a beaked nose, a small mouth, and a receding chin (micrognathia).
- Dental anomalies: These may include delayed eruption of teeth, missing teeth (hypodontia), and dental crowding.
- Proportionate dwarfism: Short stature with normal body proportions.
- Ocular abnormalities: These can include cataracts, microphthalmia (small eyes), and nystagmus.
- Skin and hair abnormalities: Thin skin and sparse hair, particularly on the scalp.
- Respiratory issues: Due to craniofacial abnormalities, individuals may experience breathing difficulties.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of Hallermann–Streiff syndrome is primarily clinical, based on the characteristic physical features. Genetic testing may be used to rule out other conditions with overlapping symptoms.
Management[edit | edit source]
There is no cure for Hallermann–Streiff syndrome, and treatment is symptomatic and supportive. Management may involve a multidisciplinary team, including:
- Ophthalmology: For the management of cataracts and other eye abnormalities.
- Dentistry: For dental anomalies.
- Orthopedics: For skeletal issues.
- Respiratory therapy: For breathing difficulties.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for individuals with Hallermann–Streiff syndrome varies depending on the severity of the symptoms and the presence of complications. With appropriate medical care, many individuals can lead relatively normal lives.
See also[edit | edit source]
- Craniofacial dysmorphisms
- Microcephaly
- Micrognathia
- Hypodontia
- Proportionate dwarfism
- Cataracts
- Microphthalmia
- Nystagmus
| Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system / musculoskeletal abnormality | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

