Retinoblastoma
(Redirected from Retinal cancer)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Retinoblastoma | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Leukocoria, strabismus, vision loss |
| Complications | Metastasis, blindness |
| Onset | Typically before age 5 |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation in RB1 gene |
| Risks | Hereditary retinoblastoma, family history |
| Diagnosis | Ophthalmoscopy, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Coats' disease, persistent fetal vasculature |
| Prevention | Genetic counseling, early screening |
| Treatment | Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, enucleation |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with early treatment |
| Frequency | 1 in 15,000 to 20,000 live births |
| Deaths | N/A |
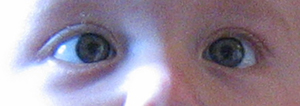
Retinoblastoma (often abbreviated as Rb) is an uncommon eye cancer that arises from the retina, the light-sensitive inner lining of the eye. Predominantly affecting young children, it represents the leading primary malignant intraocular malignancy diagnosed in this age group.[1] Although the prognosis for survival is generally favorable, the disease can result in vision loss or necessitate enucleation (removal of the eye).
Etiology and Genetics[edit | edit source]
Retinoblastoma's emergence can be ascribed to mutations in the chromosome 13's RB1 gene or MYCN gene aberrations.[2] Approximately 45% of retinoblastoma cases stem from inherited genetic mutations. The RB1 gene functions as a tumor suppressor, and its dysfunction leads to unchecked cellular growth, resulting in tumorigenesis. RB1 Gene: The hallmark of the inheritable form of retinoblastoma is the mutation in the RB1 gene situated on chromosome 13. Discovered as the inaugural tumor suppressor gene, RB1's main oncogenic restriction is achieved through the binding and inactivation of the E2F transcription factor, thereby preventing the transcription of S-phase crucial genes.[3] Such genetic anomalies can either be passed down from parents or manifest spontaneously during early fetal development. This hereditary form predominantly results in bilateral retinoblastomas and is occasionally linked with tumors in the pineal gland or other central nervous system regions, a condition termed trilateral retinoblastoma. MYCN Gene: A subset of non-familial, early-onset, unilateral retinoblastomas can be attributed to the MYCN oncogene's somatic amplification.[4]
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
The classical clinical sign of retinoblastoma is leukocoria (often termed "cat's eye reflex" or "amaurotic cat's eye reflex"), where the retina displays an anomalous white appearance when viewed through the pupil.[1] Other manifestations encompass visual impairment, a reddened and irritated eye, growth delays, developmental lags, and strabismus (referred to as "cross-eyed" or "wall-eyed"). In resource-limited settings, late presentations with an enlarged eye are commonplace.
Diagnostic Evaluation[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of retinoblastoma requires a comprehensive eye examination, usually conducted under anesthesia. While a white eye reflection (leukocoria) can suggest retinoblastoma, its presence might be due to other conditions such as Coats' disease or merely improper light reflection. Initial screening measures for infants encompass:
- Red Reflex Test: Evaluating the retina's standard reddish-orange reflection using an ophthalmoscope in dim lighting.
- Corneal Light Reflex (Hirschberg Test): Ensures the eyes are not misaligned by observing symmetrical light reflection in both corneas.
- Eye Examination: Inspecting for any structural abnormalities.
Recent advances include smartphone applications designed to identify leukocoria in photographs.[5]
Classification[edit | edit source]
Retinoblastomas can be categorized into heritable and non-heritable types. The heritable variant often manifests bilaterally, whereas the non-heritable form predominantly affects one eye (unilateral). However, the absence of familial history does not exclude the heritable form.
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Retinoblastoma's clinical manifestations can mimic other ocular conditions, necessitating its differentiation from:
- Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous
- Coats Disease
- Toxocariasis
- Retinopathy of Prematurity
Treatment and Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The treatment strategy for retinoblastoma hinges on the tumor's size, number, location, and potential metastasis. Options include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, laser therapy, and surgery. The overarching goal is the eradication of the tumor, preservation of vision, and prevention of metastasis.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Eye cancer Pediatric oncology Tumor suppressor
References[edit | edit source]
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
| Small-blue-round-cell tumors |
|---|
|
|
| Tumours of the nervous system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Note: Not all brain tumors are of nervous tissue, and not all nervous tissue tumors are in the brain (see brain metastasis).
|
| Eye neoplasm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD