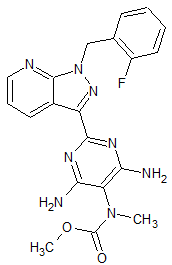
Riociguat
What is Riociguat?[edit | edit source]
- Riociguat (Adempas) is a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulator used to treat adults with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH).
What are the uses of this medicine?[edit | edit source]
This medicine is used to treat adults with: chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH)
- treated with surgery but who continue to have high pulmonary blood pressure (persistent) or it comes back after surgery (recurrent), or
- that cannot be treated with surgery.
- CTEPH is a type of high blood pressure in the arteries of your lungs caused by blood clots that narrow or block blood flow. Adempas can improve your ability to exercise and can help to improve some of your symptoms.
pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)
- PAH is a type of high blood pressure in the arteries of your lungs.
- Adempas can improve your ability to exercise, improve some of your symptoms, and help slow down the worsening of your physical condition.
How does this medicine work?[edit | edit source]
- Riociguat (rye" oh sig' ue at) is small molecular weight stimulator of soluble guanylate cyclase, an enzyme responsible for synthesis of cyclic guanine monophosphate (cyclic GMP), an important mediator of endothelial cell relaxation.
- By stimulating cyclic GMP, riociguat leads to relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells, particularly in the pulmonary vasculature.
- In humans, riociguat induces pulmonary arterial vasodilation and reduces pulmonary artery pressure.
- In several clinical trials, prolonged therapy with riociguat has been shown to improve exercise capacity and pulmonary function in patients with severe idiopathic as well as chronic thromboembolic pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
Who Should Not Use this medicine ?[edit | edit source]
This medicine cannot be used in:
- Who are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or become pregnant during treatment with Adempas
Who take:
- another medicine called a soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator (sGC).
- a nitrate medicine to treat high blood pressure or heart disease, such as nitroglycerin, or a medicine called a nitric oxide donor, such as amyl nitrite
- certain other medicines that contain sildenafil (Revatio or Viagra), tadalafil (Adcirca or Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra or Staxyn), dipyridamole, or theophylline. Revatio and Adcirca are also used to treat PAH
- Who have pulmonary hypertension associated with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (PH-IIP).
What drug interactions can this medicine cause?[edit | edit source]
- For patients receiving strong CYP and P-gp/BCRP inhibitors, consider a starting dose of 0.5 mg three times a day. Monitor for hypotension.
- Concomitant use of riociguat with strong cytochrome CYP inhibitors and P-gp/BCRP inhibitors such as azole antimycotics (for example, ketoconazole, itraconazole) or HIV protease inhibitors (such as ritonavir) increase riociguat exposure and may result in hypotension. Antacids such as aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide decrease riociguat absorption and should not be taken within 1 hour of taking Adempas.
- Co-administration of Adempas is contraindicated in patients with use of other soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulators.
- Co-administration of Adempas with nitrates or nitric oxide donors (such as amyl nitrite) in any form is contraindicated because of hypotension.
- Co-administration of Adempas with specific PDE-5 inhibitors (such as sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil) and nonspecific PDE inhibitors (such as dipyridamole or theophylline), is contraindicated because of hypotension.
- Strong inducers of CYP3A (for example, rifampin, phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital or St. John’s Wort) may significantly reduce riociguat exposure.
Is this medicine FDA approved?[edit | edit source]
- Initial U.S. Approval: 2013
How should this medicine be used?[edit | edit source]
Recommended Dosage:
- Initiate treatment at 1 mg taken three times a day.
- For patients who may not tolerate the hypotensive effect of Adempas, consider a starting dose of 0.5 mg, three times a day.
- Increase dosage by 0.5 mg at intervals of no sooner than 2-weeks as tolerated to a maximum of 2.5 mg three times a day.
Administration
- Do not take Adempas within 24 hours of sildenafil. Do not take Adempas 24 hours before or within 48 hours after tadalafil.
- Take Adempas exactly as your doctor tells you. Do not stop taking Adempas or change your dose without talking to your doctor.
- When you begin treatment with Adempas, your blood pressure should be monitored about every 2 weeks to help your doctor decide the correct dose of medicine for you.
- Your doctor may change your dose during treatment, especially when you first start taking Adempas. It is important to tell your doctor if you have any symptoms of low blood pressure during this time, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting.
- Take Adempas 3 times each day, about 6 to 8 hours apart.
- Take Adempas with or without food.
- Do not take more than a total of 7.5 mg of Adempas in 1 day unless your doctor tells you to.
- If you take a heartburn medicine (antacid) that contains aluminum hydroxide or magnesium hydroxide, do not take it within 1 hour of taking Adempas.
- If you take too much Adempas, call your doctor right away or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
- If you miss a dose, take your next dose of Adempas at the regular time.
- If you miss 3 or more days of treatment with Adempas, call your doctor for instructions before you restart Adempas.
- Tablets may be crushed and mixed with water or soft foods for patients who have difficulty swallowing.
What are the dosage forms and brand names of this medicine?[edit | edit source]
This medicine is available in fallowing doasage form:
- As Tablets: 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg and 2.5 mg
This medicine is available in fallowing brand namesː
- Adempas
What side effects can this medication cause?[edit | edit source]
The most common side effects of this medicine include:
- headache
- dizziness
- indigestion
- swelling of your hands, legs, feet, and ankles (peripheral edema)
- nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting
Adempas can cause serious side effects including:
- Serious birth defects
- Reduced blood pressure
- Increased risk of bleeding, including bleeding from the respiratory tract
- Worsening of symptoms in people with Pulmonary Veno-Occlusive Disease (PVOD).
What special precautions should I follow?[edit | edit source]
- Based on data from animal reproduction studies, Adempas may cause embryo-fetal toxicity when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated in females who are pregnant. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Obtain a pregnancy test before the start of treatment, monthly during treatment, and for one month after stopping treatment. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ADEMPAS and for at least one month after the last dose.
- Do not drive, operate machinery, or do other activities that require mental alertness or coordination until you know how Adempas affects you. Talk with your doctor if you are concerned about when it is safe for you to do these activities.
- Adempas may not work as well if you smoke during treatment. Tell your doctor if you stop smoking or start smoking during treatment with Adempas, because your dose of Adempas may need to be changed.
- Adempas reduces blood pressure. Consider a dose reduction if patient develops signs or symptoms of hypotension.
- In the placebo-controlled clinical trials, serious bleeding occurred in 2.4% of patients taking Adempas.
- Pulmonary vasodilators may significantly worsen the cardiovascular status of patients with pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD). Therefore, administration of Adempas to such patients is not recommended.
What to do in case of emergency/overdose?[edit | edit source]
Management of overdosage:
- In cases of overdose, blood pressure should be closely monitored and supported as appropriate.
- Based on extensive plasma protein binding, riociguat is not expected to be dialyzable.
Can this medicine be used in pregnancy?[edit | edit source]
- Adempas may cause embryo-fetal toxicity and miscarriage when administered to a pregnant woman and is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Can this medicine be used in children?[edit | edit source]
- Safety and effectiveness of Adempas in pediatric patients have not been established.
What are the active and inactive ingredients in this medicine?[edit | edit source]
- Active ingredient: riociguat
- Inactive ingredients: cellulose microcrystalline, crospovidone, hypromellose 5cP, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, sodium laurylsulfate, hydroxypropylcellulose, hypromellose 3cP, propylene glycol, titanium dioxide. Adempas 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg and 2.5 mg tablets also contain ferric oxide yellow. Adempas 2 mg and 2.5 mg tablets also contain ferric oxide red.
Who manufactures and distributes this medicine?[edit | edit source]
Manufactured for: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. Whippany, NJ 07981 Manufactured in Germany
What should I know about storage and disposal of this medication?[edit | edit source]
- Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions are permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F)
| Medications used in the management of pulmonary arterial hypertension (B01, C02) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Pulmonary Disease Agents
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Agents
- Anticholinergic Agents
- Beta-2 Adrenergic Agonists
- Corticosteroids
- Miscellaneous
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Agents
- Endothelin Receptor Antagonists
- Phosphodiesterase Type 5 (PDE5) Inhibitors
- Prostacyclin Analogs
- Miscellaneous
- Pulmonary Fibrosis Agents
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Deepika vegiraju