Congenital rubella syndrome
(Redirected from Congenital rubella)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Congenital rubella syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Deafness, cataracts, heart defects, intellectual disability |
| Complications | Developmental delay, autism, diabetes mellitus |
| Onset | Prenatal |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Rubella virus infection during pregnancy |
| Risks | Unvaccinated mothers |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis, serology |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | Rubella vaccine |
| Treatment | Supportive care |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Rare in countries with high vaccination rates |
| Deaths | N/A |
Alternate names[edit | edit source]
Rubella congenital; Congenital rubella syndrome; CRS
Definition[edit | edit source]
Congenital rubella refers to the group of birth defects that occur in an infant whose mother is infected with the virus that causes German measles (rubella) during pregnancy.
Cause[edit | edit source]
- Congenital rubella occurs when the rubella virus in the mother affects the developing baby in the first 3 months of pregnancy.
- After the fourth month, if the mother has a rubella infection, it is less likely to harm the developing baby.
Pregnant women and their unborn babies are at risk if:
- They are not vaccinated for rubella
- They have not had the disease in the past
Signs and symptoms[edit | edit source]
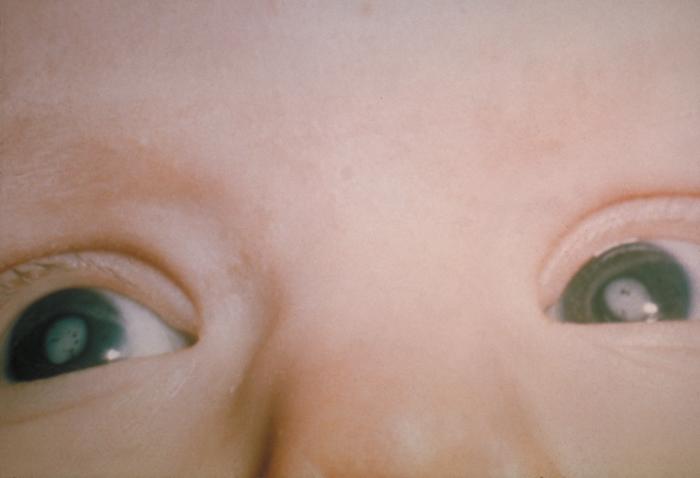
The most common problems are hearing loss due to damage to the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain (sensorineural hearing loss), ocular abnormalities (cataract, infantile glaucoma, and pigmentary retinopathy) and heart problems. Other symptoms and signs may include intrauterine growth retardation, prematurity, stillbirth, miscarriage, neurological problems (intellectual disability, low muscle tone, very small head), liver and spleen enlargement (hepatosplenomegaly), jaundice, skin problems, anemia, hormonal problems, and other issues.
Clinical presentation[edit | edit source]
For most diseases, symptoms will vary from person to person. People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. 80%-99% of people have these symptoms
- Cataract(Clouding of the lens of the eye)
- Intrauterine growth retardation(Prenatal growth deficiency)
- Neurological speech impairment(Speech disorder)
- Sensorineural hearing impairment
30%-79% of people have these symptoms
- Abnormality of retinal pigmentation
- Abnormality of the fontanelles or cranial sutures
- Abnormality of the pulmonary artery(Abnormality of lung artery)
- Anemia(Low number of red blood cells or hemoglobin)
- Aplasia/Hypoplasia of the iris(Absent/small iris)
- Atrial septal defect(An opening in the wall separating the top two chambers of the heart)
- Glaucoma
- Hepatomegaly(Enlarged liver)
- Intellectual disability(Mental deficiency)
- Microcephaly(Abnormally small skull)
- Microphthalmia(Abnormally small eyeball)
- Muscular hypotonia(Low or weak muscle tone)
- Nystagmus(Involuntary, rapid, rhythmic eye movements)
- Patent ductus arteriosus
- Short stature(Decreased body height)
- Skin rash
- Spastic diplegia
- Splenomegaly(Increased spleen size)
- Strabismus(Cross-eyed)
- Thrombocytopenia(Low platelet count)
- Ventricular septal defect(Hole in heart wall separating two lower heart chambers)
- Visual impairment(Impaired vision)
5%-29% of people have these symptoms
- Abnormality of the metaphysis(Abnormality of the wide portion of a long bone)
- Corneal opacity
- Jaundice(Yellow skin)
- Seizure
- Type I diabetes mellitus(Type 1 diabetes)
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The baby's health care provider will run blood and urine tests to check for the virus.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
There is no specific treatment for congenital rubella. The treatment is symptom-based.
| Skin infections, symptoms and signs related to viruses | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Conditions originating in the perinatal period / fetal disease | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Vertically transmitted infections | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NIH genetic and rare disease info[edit source]
Congenital rubella syndrome is a rare disease.
| Rare and genetic diseases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rare diseases - Congenital rubella syndrome
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Deepika vegiraju, Prab R. Tumpati, MD



