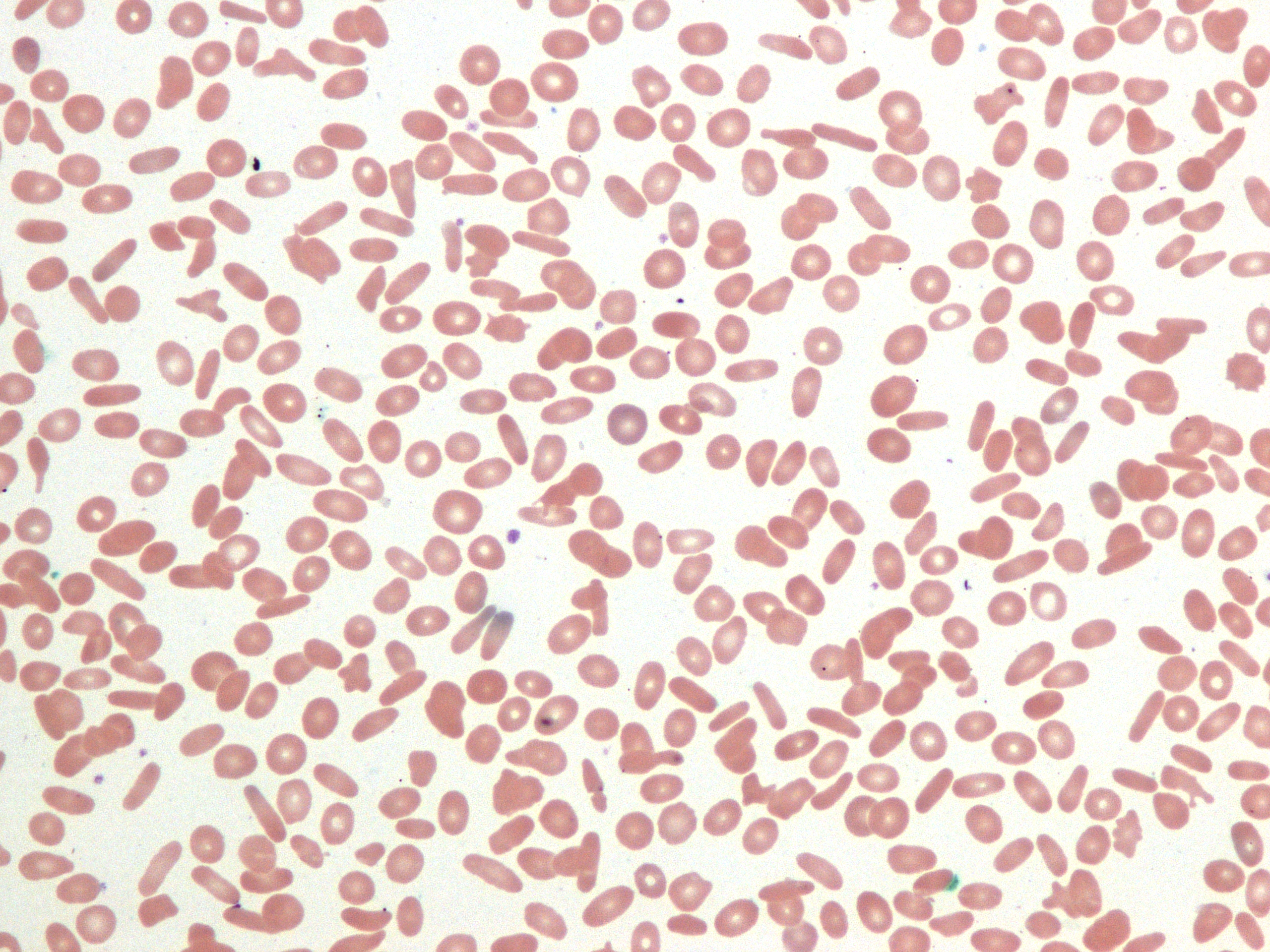
Hereditary elliptocytosis
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hereditary elliptocytosis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Ovalocytosis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hemolytic anemia, jaundice, splenomegaly |
| Complications | Gallstones, splenic rupture |
| Onset | Usually in infancy or childhood |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutations in spectrin, ankyrin, or band 3 protein |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Blood smear, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Hereditary spherocytosis, pyruvate kinase deficiency |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Folic acid supplementation, splenectomy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | 1 in 2,000 to 1 in 4,000 individuals |
| Deaths | N/A |
Other names:Elliptocytosis - hereditary
Hereditary elliptocytosis (HE) refers to a group of inherited blood conditions where the red blood cells are abnormally shaped.
Epidemiology[edit | edit source]
Elliptocytosis affects about 1 in every 2,500 people of northern European heritage. It is more common in people of African and Mediterranean descent. You are more likely to develop this condition if someone in your family has had it.
Cause[edit | edit source]
Hereditary elliptocytosis is caused by a genetic change in either the EPB41, SPTA1, or SPTB gene. Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis, a related condition, is caused by two mutations in these genes.
Inheritance[edit | edit source]

It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis is a related condition with more serious symptoms, and is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The symptoms of hereditary elliptocytosis may be different from person to person. Symptoms may appear at any age. Many people who have this condition have no symptoms at all. Most people with this condition have mild symptoms , while a few have more serious symptoms. Not everyone with hereditary elliptocytosis will have the same symptoms. The most common signs and symptoms of hereditary elliptocytosis are:
- Anemia
- fatigue
- shortness of breath
- Gallstones
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)
- Very low blood levels after an infection (aplastic crisis)
Hydrops fetalis, an abnormal buildup of fluids in the body of a fetus, has been reported, as well as more serious anemia in early childhood For most diseases, symptoms will vary from person to person. People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. 30%-79% of people have these symptoms
- Elliptocytosis
- Increased red cell osmotic fragility
5%-29% of people have these symptoms
- Congenital hemolytic anemia
- Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia
- Prolonged neonatal jaundice(Prolonged yellowing of skin in newborn)
- Reticulocytosis(Increased immature red blood cells)
- Splenomegaly(Increased spleen size)
- Stomatocytosis
1%-4% of people have these symptoms
- Abdominal pain(Pain in stomach)
- Chills
- Cholelithiasis(Gallstones)
- Fever
- Frontal bossing
- Hydrops fetalis
- Postnatal growth retardation(Growth delay as children)
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
An exam by your health care provider may show an enlarged spleen. The following test results may help diagnose the condition:
- Bilirubin level may be high.
- Blood smear may show elliptical red blood cells.
- Complete blood count (CBC) may show anemia or signs of red blood cell destruction.
- Lactate dehydrogenase level may be high.
- Imaging of the gallbladder may show gallstones.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for hereditary elliptocytosis is often not necessary. When symptoms are severe enough, some people with this condition will be treated with transfusion or even removal of the spleen (splenectomy). Surgery to remove the spleen may decrease the rate of red blood cell damage.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
Hereditary elliptocytosis is generally mild and very rarely life threatening.
| Diseases of red blood cells | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Genetic disorder, membrane: Solute carrier disorders | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
see also solute carrier family
|
NIH genetic and rare disease info[edit source]
Hereditary elliptocytosis is a rare disease.
| Rare and genetic diseases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rare diseases - Hereditary elliptocytosis
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Deepika vegiraju, Prab R. Tumpati, MD


