Pulmonary aspiration
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Pulmonary aspiration | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain, fever |
| Complications | Aspiration pneumonia, lung abscess, chronic lung disease |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Gastroesophageal reflux disease, dysphagia, sedation, anesthesia |
| Risks | Neurological disorders, alcohol intoxication, elderly age, reduced consciousness |
| Diagnosis | Chest X-ray, bronchoscopy, sputum culture |
| Differential diagnosis | Pneumonia, pulmonary edema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| Prevention | Head elevation, swallowing therapy, dietary modifications |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, supportive care, oxygen therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depending on severity and complications |
| Frequency | Common in hospitalized patients |
| Deaths | N/A |
Pulmonary aspiration[edit | edit source]
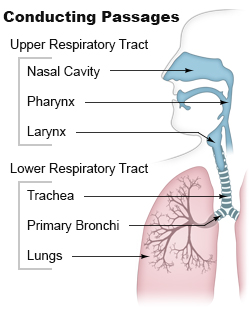
Pulmonary aspiration is the entry of material (such as phlegm, food or drink, or stomach contents) from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract into the larynx (voice box) and lower respiratory tract, the portions of the respiratory system from the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs. A person may either inhale the material, or it may be delivered into the tracheobronchial tree during positive pressure ventilation. When pulmonary aspiration occurs during eating and drinking, the aspirated material is often colloquially referred to as "going down the wrong pipe."
Causes[edit | edit source]
Consequences of pulmonary aspiration range from no injury at all, to chemical pneumonitis, to lung abscess, to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). The risk of pulmonary aspiration is relatively high in individuals with a reduced level of consciousness (as a result of intoxication or anaesthetic). In healthy adults, the risk of aspiration is lowest when a person is sitting or standing and awake.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of pulmonary aspiration include coughing, wheezing, fever, shortness of breath, rapid breathing, chest pain, and a bluish coloration of the skin (cyanosis).
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of pulmonary aspiration is based on patient history and often confirmed by physical examination and chest x-ray.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for pulmonary aspiration depends on the severity of the condition and the symptoms. It may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, bronchodilators for wheezing, oxygen therapy for low oxygen levels, and in severe cases, mechanical ventilation.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Prevention strategies for pulmonary aspiration include maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding over sedation, proper positioning of the body during and after eating, and specific interventions by healthcare professionals such as speech therapists and occupational therapists.
See also[edit | edit source]
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
References[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
| Diseases of the respiratory system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Infectious diseases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This infectious diseases related article is a stub.
|
| Emergency medicine | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD


