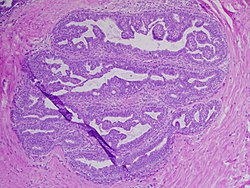
Papilloma
Benign epithelial tumor characterized by finger-like projections
| Papilloma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Papillomata |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | Oncology, Dermatology, Pathology |
| Symptoms | Small, exophytic growths with a cauliflower-like appearance |
| Complications | Potential for irritation or infection |
| Onset | Varies, can be weeks to years |
| Duration | May persist without treatment |
| Types | Squamous cell papilloma, Intraductal papilloma, Urothelial papilloma |
| Causes | Human papillomavirus (HPV), unknown in some cases |
| Risks | HPV exposure, weakened immune system |
| Diagnosis | Histopathology, Biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Verruca vulgaris, Condyloma acuminatum, Focal epithelial hyperplasia |
| Prevention | HPV vaccination, good hygiene |
| Treatment | Surgical excision, laser therapy |
| Medication | None required in most cases |
| Prognosis | Benign, low recurrence risk after excision |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | None directly related |
Papilloma (plural: papillomas or papillomata) is a benign epithelial tumor that grows exophytically (outwardly projecting), forming nipple-like or finger-like fronds. The term "papilla" in this context refers to the growth projection itself, not necessarily a tumor on an existing papilla (e.g., nipple).
Papillomas are often associated with human papillomavirus (HPV), which can lead to conditions such as warts and, in some cases, cervical cancer. However, not all papillomas are caused by HPV, and many have unknown etiologies.
Signs and Symptoms[edit | edit source]
A benign papillomatous tumor is derived from the epithelium and appears as a cauliflower-like projection that arises from a mucosal or cutaneous surface. Features include:
- Color: White or normal skin color.
- Size: Typically 1–5 cm in diameter.
- Shape: Pedunculated (stalk-like) or sessile (flat-based).
- Location: Common in the palate-uvula area, tongue, lips, and skin.
- Duration: Can persist for weeks to years.
- Sex prevalence: No significant gender predilection.
Causes[edit | edit source]
Many papillomas are linked to human papillomavirus (HPV), specifically types 6 and 11, which are commonly associated with squamous cell papillomas.
Types[edit | edit source]
Papillomas can occur in various tissues and structures, including:
- Squamous cell papilloma – Often found in the skin and oral cavity.
- Intraductal papilloma – Found in the breast ducts, associated with nipple discharge.
- Urothelial papilloma – A rare, benign bladder tumor.
- Inverted papilloma – Found in the nasal cavity and sinuses.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Papillomas are diagnosed through:
- Clinical examination – Based on appearance and location.
- Histopathology – Microscopic examination of biopsied tissue.
- Immunoperoxidase stains – Used to detect HPV antigens in suspected cases.
Differential Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Conditions that may mimic papilloma include:
- Intraoral verruca vulgaris – Common wart.
- Condyloma acuminatum – Genital wart caused by HPV.
- Focal epithelial hyperplasia – HPV-associated mucosal lesion.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
Papillomas are benign with no evidence of malignancy or premalignant potential. However, persistent lesions should be evaluated to rule out malignancy.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Papillomas are usually removed with conservative surgical excision, which has a low recurrence rate. Other treatment options include:
- Laser ablation – Useful for warts and oral lesions.
- Cryotherapy – Freezing treatment, effective for skin lesions.
- Electrocautery – Burning off the lesion with electrical current.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
While not all papillomas are preventable, those linked to HPV can be reduced by:
- HPV vaccination – Protects against high-risk HPV strains.
- Safe hygiene practices – Reduces risk of viral spread.
See Also[edit | edit source]
- Skin tag
- Wart
- Inverted papilloma
- Squamous cell papilloma
- Urothelial papilloma
- Intraductal papilloma
- Papillomavirus
- Human papillomavirus
External Links[edit | edit source]
- Choroid Plexus Papilloma - Palmer, Cheryl Ann and Daniel Keith Harrison; EMedicine
| Glandular and epithelial cancer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Human papillomavirus | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD
