Persistent edema of rosacea
(Redirected from Chronic upper facial erythematous edema)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Persistent edema of rosacea | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Morbihan disease, Morbihan syndrome |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Chronic facial swelling, erythema, papules, pustules |
| Complications | Lymphedema, disfigurement |
| Onset | Typically in adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Unknown, associated with rosacea |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, environmental factors |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Angioedema, melkersson-rosenthal syndrome, sarcoidosis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Oral antibiotics, isotretinoin, corticosteroids, surgery |
| Medication | Doxycycline, isotretinoin |
| Prognosis | Variable, often chronic |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
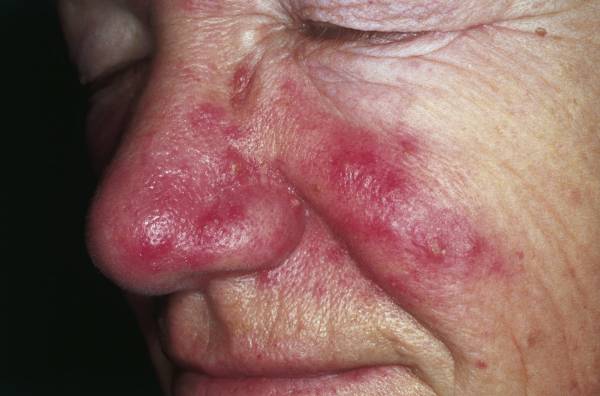
Persistent edema of rosacea is a rare subtype of rosacea, a chronic skin condition characterized by facial redness, small and superficial dilated blood vessels, papules, pustules, and swelling. Persistent edema, or swelling, is a less common symptom of rosacea that can occur in some individuals.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The primary symptom of persistent edema of rosacea is swelling of the skin that lasts for an extended period. This can occur in any area affected by rosacea, but it is most commonly seen on the face. The swelling may be accompanied by other symptoms of rosacea, such as redness, papules and pustules, and visible blood vessels.
Causes[edit | edit source]
The exact cause of persistent edema of rosacea is unknown. However, it is thought to be related to the inflammation caused by rosacea. This inflammation can damage the lymphatic system, which is responsible for draining fluid from tissues. This can result in fluid build-up, leading to persistent edema.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of persistent edema of rosacea is typically based on the clinical presentation of the patient. A dermatologist may also perform a skin biopsy to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as cellulitis or lymphedema.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for persistent edema of rosacea typically involves managing the underlying rosacea. This can include topical treatments, oral medications, and lifestyle changes to reduce triggers. In some cases, surgery may be recommended to remove excess tissue.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

