Evidence-based medicine
(Redirected from Evidence-based health care)
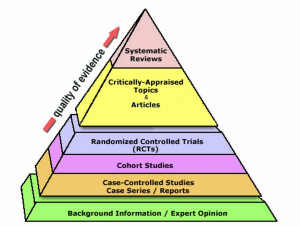 Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is an approach to medical practice that emphasizes the application of the scientific method to healthcare decision-making. As described by the Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, "Evidence-based medicine is the conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients." This involves integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence derived from systematic research.[1]
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) is an approach to medical practice that emphasizes the application of the scientific method to healthcare decision-making. As described by the Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, "Evidence-based medicine is the conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients." This involves integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence derived from systematic research.[1]
Overview[edit | edit source]
Evidence-based medicine employs techniques and tools from fields like science, engineering, and statistics. Techniques such as meta-analysis of scientific literature, risk-benefit analysis, and randomized controlled trials are foundational to the EBM process. The underlying principle is that healthcare professionals should utilize the most current and rigorous evidence available when making clinical decisions.
EBM has three core components:
- Individualized patient care, in which treatments are chosen based on the best available research tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of individual patients.
- Systemic analysis of medical literature, where studies on specific topics are critically reviewed and assessed for their quality and relevance. This can be facilitated through human-driven processes like a journal club or technologically-driven ones using data mining and information technology.
- Promotion and advocacy of EBM principles to a broader audience, encompassing patients, the general public, educational institutions, and continuing education for healthcare professionals.
- One significant shift due to EBM is the relegation of ex cathedra statements or "expert opinion" to one of the lower tiers of evidence. Instead of relying solely on tradition or authority, healthcare decisions increasingly depend on scientific research.
History[edit | edit source]
The concept of evaluating medical interventions has ancient roots, but the formalization of evidence-based practices took off in the 20th century. A pivotal figure in this movement was Professor Archie Cochrane, a Scottish epidemiologist. His influential book Effectiveness and Efficiency: Random Reflections on Health Services published in 1972, emphasized the importance of evidence in healthcare decisions. His advocacy and contributions were commemorated with the establishment of the Cochrane Centres and the international Cochrane Collaboration. Another significant contribution came from the McMaster University research group led by pioneers David Sackett and Gordon Guyatt. The term "evidence-based medicine" made its first official appearance in the medical literature in 1992 through a paper by Guyatt and colleagues.
Qualification of evidence[edit | edit source]
EBM classifies clinical evidence into various categories based on their susceptibility to biases. For instance, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials are viewed as providing the strongest evidence. On the other hand, anecdotal evidence like patient testimonials or expert opinions are considered weak due to biases and other inherent flaws.
Central to EBM is the clinician's skill in interpreting, applying, and communicating scientific findings to patients. A significant metric used in EBM is the number needed to treat (NNT), which quantifies the effectiveness of a treatment. Different systems, such as those proposed by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and the UK National Health Service, stratify evidence based on quality.
Categories of recommendations[edit | edit source]
When clinical guidelines or other publications make recommendations, they categorize these based on the evidence's quality and the balance of risk versus benefit. Different organizations, such as the U.S. Preventive Service Task Force and the Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine, have proposed systems for grading recommendations.
Limitations of available evidence[edit | edit source]
EBM recognizes that not all evidence is readily accessible, which can limit its effectiveness. Unpublished negative trials, non-representative studies in medical journals due to conflicts of interest, and the potential overperformance of treatments in clinical studies due to rigorous monitoring are some challenges faced by EBM.
Criticism of evidence-based medicine[edit | edit source]
Despite EBM's growing acceptance as a gold standard in clinical practice, it faces criticism. Some argue that EBM focuses excessively on populations at the expense of individual patients. Critics also highlight the difficulties in generalizing results from controlled trials to real-world scenarios, biases introduced due to funding sources, and the potential misuse of EBM guidelines in managed healthcare systems.
See also[edit | edit source]
- Adverse drug reaction
- Adverse effect (medicine)
- Clinical trials with surprising outcomes
- Consensus (medical)
- Epidemiology
- Guideline (medical)
- History of medicine
- Medical algorithm
- Medical research
- Nocebo
- Placebo (origins of technical term)
- Systematic Reviews
- Evidence-based management
- Evidence based dentistry
External links[edit | edit source]
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
Medical education in the United States
|
CME in Internal medicine CME Resources | Grand Rounds - webcasts and videos. |
| Cardiology - Endocrinology - Gastroenterology - Hematology - Infectious diseases - Nephrology - Oncology - Pulmonology - Rheumatology |
| CME in Health sciences |
| Anesthesiology - Dermatology - Emergency Medicine CME Resources - General practice - Intensive care - Internal Medicine - Neurology CME Resources - Obstetrics & Gynecology - Pediatrics - Psychiatry - Radiology - Surgery |
| CME in Surgery |
| General surgery - Cardiothoracic surgery - Neurosurgery - Ophthalmology - Orthopedic surgery - Otolaryngology CME Resources (ENT) - Plastic surgery - Urology CME Resources - Vascular surgery |
< Free Medical Resources | Free CME Webcasts and Videos on the Internet | Free CME on the Internet
| Health care quality | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Medicine | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Clinical research and experimental design | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
- ↑ Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. (Date). About the Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. Retrieved (Date).
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD
