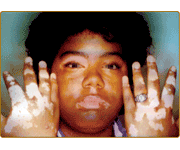
Vitiligo
(Redirected from Leukoderma)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Vitiligo | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Depigmentation of patches of skin |
| Complications | Psychological stress, social stigma |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | Non-segmental vitiligo, Segmental vitiligo |
| Causes | Autoimmune disease, genetic predisposition |
| Risks | Family history, autoimmune diseases |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis, Wood's lamp |
| Differential diagnosis | Pityriasis alba, tinea versicolor, leprosy |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Phototherapy, topical corticosteroids, depigmentation |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | 0.5–1% of the population |
| Deaths | N/A |
Vitiligo is a condition in which patches of skin on the body lose their color; thought to be caused by the immune system attacking the skin tissues, causing the absence of melanin.
Overview of Vitiligo[edit | edit source]
Vitiligo (vit-ill-EYE-go) is a skin disorder that causes patches of skin to turn white due to the destruction of melanocytes (ma-LAN-o-sites), the cells responsible for producing pigment or color. Although there is no cure for vitiligo, treatment options may help make skin tone appear more even. Vitiligo can either spread or remain stable, with nonsegmental vitiligo typically spreading while segmental vitiligo does not. Doctors are unable to predict the progression of the condition. People with vitiligo and their family members may have a higher risk of developing certain autoimmune diseases.
Who Gets Vitiligo?[edit | edit source]
Vitiligo can affect anyone, but it is most noticeable in individuals with dark skin. For most people, the white patches begin to appear in their 20s. Vitiligo seems to be more common in those with a family history of the disorder or with certain autoimmune diseases, such as: Hyperthyroidism Adrenocortical insufficiency Alopecia areata Pernicious anemia However, most people with vitiligo do not have an autoimmune disease or a family history of the disorder.
Symptoms of Vitiligo[edit | edit source]
The primary symptom of vitiligo is patches of white or depigmented skin. The depigmented patches are most common on sun-exposed body parts, including hands, feet, arms, and face. Depigmented patches may also appear on and around the eyes, armpits, groin, navel, genitals, and rectum. Vitiligo usually develops in one of these patterns: Segmental (or unilateral) pattern, where the white patches are on only one side of the body. Nonsegmental (or bilateral or generalized) pattern, where the white patches appear symmetrically on both sides of the body. This is the most common pattern. Additional symptoms may include patches of white or gray hair, white eyelashes, or white eyebrows. People with dark skin may have lighter areas inside their mouths. Some individuals with vitiligo may develop uveitis, inflammation of a part of the eye.
Causes of Vitiligo[edit | edit source]
The exact cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it may be an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the body's own cells. Some people have reported developing vitiligo or experiencing a worsening of the condition after sunburns or emotional distress, but researchers are uncertain if these factors caused vitiligo.
Diagnosis of Vitiligo[edit | edit source]
To diagnose vitiligo, a doctor will typically examine the skin, ask questions to rule out other illnesses, and perform tests. Some questions a doctor may ask include: Do any of your family members have vitiligo? Do you or any of your family members have any autoimmune diseases? Did you have a rash, sunburn, or other skin problem before the white patches appeared? Did you experience a stressful event or physical illness? Did your hair turn gray before age 35? Are you sensitive to the sun? Tests might include: A biopsy, which involves taking a small sample of skin to be examined. Under a microscope, doctors can usually see a complete absence of melanocytes in the depigmented skin of a person with vitiligo. Blood tests to check for autoimmune diseases. An eye exam to check for uveitis, inflammation of part of the eye that sometimes occurs with vitiligo.
Treatment of Vitiligo[edit | edit source]
Vitiligo is not usually medically harmful, but the white patches can cause emotional distress. Most treatments aim to restore color to the white patches of skin. For some people, treatment helps make the skin color look more even, but many treatments can have unwanted side effects. Treatments can take a long time, and sometimes they don’t work. Medical treatments can include:
- Medicines or medicated skin creams, such as corticosteroids, that may be able to return color to the white patches of skin. This is particularly effective in early stages of the disease.
- Light or laser treatments.
- A combination of ultraviolet light treatment and medicine known as psoralen photochemotherapy or psoralen and ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy. This involves taking or applying the drug psoralen, which reacts with ultraviolet light to cause your skin to darken. With this type of therapy, it is very important to limit your exposure to sunlight.
- Depigmentation, or removing color from dark areas of the skin so they match the white patches. This may be recommended for people who have vitiligo on more than half of their bodies. Depigmentation tends to be permanent, is time consuming, and will make you unusually sensitive to sunlight.
- Tattooing small areas of skin.
- Surgical techniques when topical creams and light therapy do not work. Surgery is typically not recommended for people who scar easily or develop keloids.
Who Treats Vitiligo?[edit | edit source]
A number of doctors can diagnose and treat vitiligo. These include:
- Dermatologists, who treat skin problems.
- Primary care physicians or internists.
- Other specialists, such as opthamologists (who treat eye problems) may also provide care.
Living With Vitiligo[edit | edit source]
Health care professionals can recommend treatments for your vitiligo, but you can also take part in your own care.
- Sunscreen can help protect your skin from long-term damage.
- Cosmetics, such as self-tanning lotions or dyes, can cover depigmented patches.
- Some people with vitiligo are upset or depressed about the changes in their appearance. Counseling and support can help you cope with the disorder.
To better manage vitiligo:
- Find a doctor who knows how to treat vitiligo. The doctor should also be a good listener and provide emotional support.
- Learn about the disorder and treatments to help you make decisions about care.
- Talk with other people who have vitiligo. A vitiligo group may help you find a support group in your area.
- Your family and friends can also support you.
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
| Diseases of the skin and appendages by morphology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Pigmentation disorders/Dyschromia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD