Systemic scleroderma
(Redirected from Systemic sclerosis)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Systemic scleroderma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Systemic sclerosis |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology |
| Symptoms | Skin thickening, Raynaud's phenomenon, joint pain, esophageal dysmotility, pulmonary fibrosis |
| Complications | Pulmonary hypertension, renal crisis, heart failure |
| Onset | Typically between ages 30 and 50 |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Autoimmune disease |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, environmental factors |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, autoantibody testing, skin biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Localized scleroderma, lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Immunosuppressive therapy, physical therapy, antifibrotic agents |
| Medication | Methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, cyclophosphamide |
| Prognosis | Variable; depends on organ involvement |
| Frequency | 1 in 10,000 people |
| Deaths | |
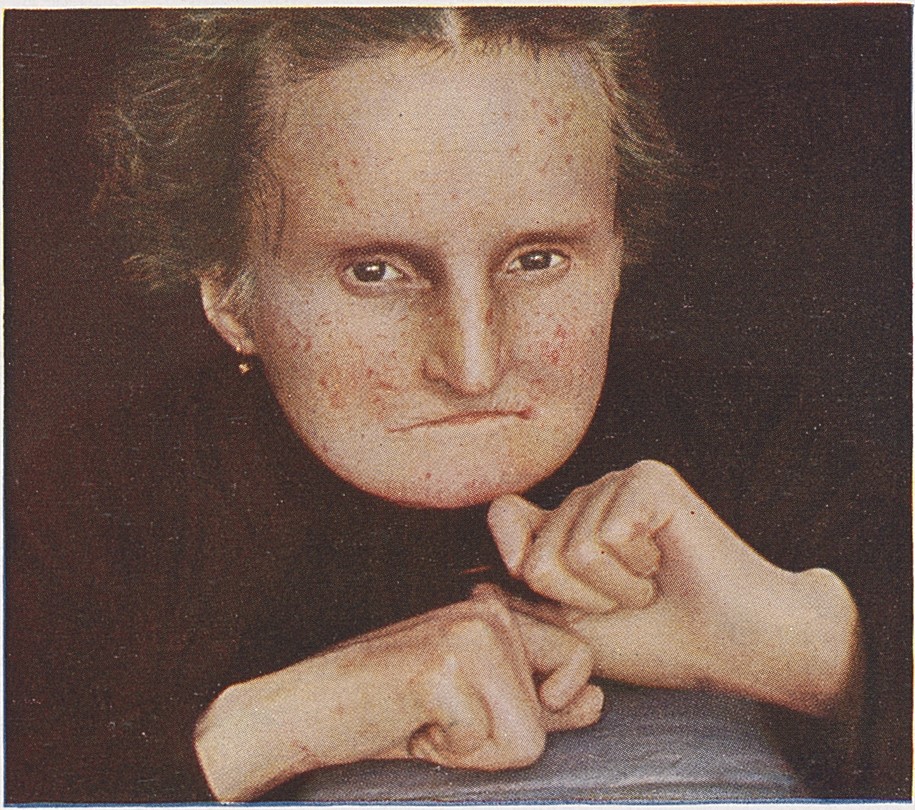
A chronic connective tissue disease



Systemic scleroderma, also known as systemic sclerosis, is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by fibrosis (thickening and hardening) of the skin and internal organs. It is a complex condition that affects the connective tissue and can lead to significant morbidity and mortality.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
Systemic scleroderma is primarily characterized by excessive collagen deposition in the skin and other organs. The exact cause of the disease is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. The disease process involves autoimmunity, vascular dysfunction, and fibrosis.
Autoimmunity[edit | edit source]
In systemic scleroderma, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, leading to inflammation and fibrosis. Autoantibodies such as anti-centromere and anti-Scl-70 are often present in patients and can be used as markers for diagnosis.
Vascular Dysfunction[edit | edit source]
Vascular abnormalities are a hallmark of systemic scleroderma. Patients often experience Raynaud's phenomenon, which is characterized by episodic vasospasm of the fingers and toes. Over time, persistent vascular damage can lead to digital ulcers and pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Fibrosis[edit | edit source]
Fibrosis in systemic scleroderma results from the overproduction of collagen by fibroblasts. This leads to thickening and hardening of the skin and can affect internal organs such as the lungs, heart, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract.
Clinical Features[edit | edit source]
The clinical presentation of systemic scleroderma is highly variable and can range from mild skin involvement to severe multi-organ disease.
Skin Involvement[edit | edit source]
The skin changes in systemic scleroderma typically begin with edema and progress to sclerosis. The skin becomes tight, shiny, and may restrict movement. Telangiectasia and calcinosis can also occur.
Musculoskeletal System[edit | edit source]
Patients may experience joint pain, stiffness, and muscle weakness. Arthralgia and myopathy are common symptoms.
Pulmonary Involvement[edit | edit source]
Lung involvement is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in systemic scleroderma. Interstitial lung disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension are common complications.
Gastrointestinal Tract[edit | edit source]
The gastrointestinal tract can be affected at any level, leading to symptoms such as dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and malabsorption.
Renal Involvement[edit | edit source]
Renal crisis, characterized by sudden onset of hypertension and renal failure, is a serious complication of systemic scleroderma.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of systemic scleroderma is based on clinical features, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. The presence of specific autoantibodies can aid in diagnosis. Skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
There is no cure for systemic scleroderma, but treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Immunosuppressive therapy, vasodilators, and antifibrotic agents are commonly used. Physical therapy and occupational therapy can help maintain mobility and function.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis of systemic scleroderma varies depending on the extent of organ involvement and the presence of complications. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes.
See also[edit | edit source]
| Systemic connective tissue disorders | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD



