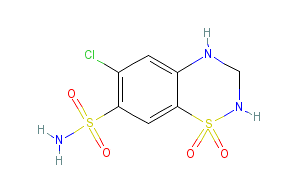
Aliskiren/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide
Aliskiren/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide (Amturnide) is a combination of aliskiren, a renin inhibitor, amlodipine besylate, a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, and hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), a thiazide diuretic used for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure.
What are the uses of this medicine?[edit | edit source]
- Aliskiren/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide (Amturnide) used to lower blood pressure (hypertension).
- Amturnide is not for use as the first medicine to treat your high blood pressure.
Amturnide contains 3 different prescription medicines:
- aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor (DRI)
- amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker (CCB) and
- hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), a diuretic (water pill)
How does this medicine work?[edit | edit source]
- The effects of combined treatment of aliskiren, amlodipine and HCTZ is combination of actions of these three agents on different but complementary mechanisms that regulate blood pressure.
- Together, inhibition of the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS), inhibition of calcium channel-mediated vasoconstriction, and increase of sodium chloride excretion lowers blood pressure to a greater degree than the individual components.
Aliskiren:
- Aliskiren (al' is key' ren) is a direct inhibitor of renin and acts to inhibit its ability to convert angiotensinogen to angiotensin 1, an early step in the renin-angiotensin system pathway.
- By inhibiting renin and the subsequent production of angiotensin II and aldosterone release, aliskiren results in a decrease in peripheral vasoconstriction and increase in sodium excretion.
- Aliskiren is effective in lowering blood pressure and can be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive medications, including other inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system such as the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and the angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
Amlodipine:
- Amlodipine (am loe' di peen) belongs to the dihydropyridine class of calcium channel blockers and is used in the treatment of both hypertension and angina pectoris.
- Like other calcium channel blockers, amlodipine acts by blocking the influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle cells during membrane depolarization.
- This action causes relaxation of vascular and arterial smooth muscle cells, resulting in arterial vasodilation and a decrease in cardiac work and oxygen consumption.
HCTZ:
- HCTZ is a thiazide diuretic.
- Thiazides affect the renal tubular mechanisms of electrolyte reabsorption, directly increasing excretion of sodium and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts.
- Indirectly, the diuretic action of HCTZ reduces plasma volume, with consequent increases in plasma renin activity, increases in aldosterone secretion, increases in urinary potassium loss, and decreases in serum potassium.
Who Should Not Use this medicine ?[edit | edit source]
This medicine cannot be used in patients:
- Who are pregnant
- who have diabetes and are taking a kind of medicine called an angiotensin-receptor-blocker or angiotensin-converting-enzyme-inhibitor.
- who have low or no urine output
- who are allergic to any ingredients in Amturnide or other medicines that contain sulfonamide.
What drug interactions can this medicine cause?[edit | edit source]
- Avoid concomitant use with Cyclosporine.
- Avoid concomitant use with Itraconazole.
- NSAIDS use may lead to increased risk of renal impairment and loss of antihypertensive effect.
- If simvastatin is co-administered with amlodipine, do not exceed doses greater than 20 mg daily of simvastatin.
- When administered concurrently with antidiabetic drugs (oral agents and insulin) dosage adjustment of the antidiabetic drug may be required.
- Cholestyramine and Colestipol may reduce absorption of thiazides. Hydrochlorothiazide is administered at least 4 hours before or 4-6 hours after the administration of resins would
- potentially minimize the interaction.
- Increased risk of lithium toxicity when used with diuretics. Monitor serum lithium concentrations during concurrent use.
Is this medicine FDA approved?[edit | edit source]
- It was approved for medical use in the United States in December 2010.
How should this medicine be used?[edit | edit source]
Recommended dosage:
- Dose once-daily.
- The dosage may be increased after 2 weeks of therapy.
- The maximum recommended dose of Amturnide is 300/10/25 mg.
Administration:
- Take Amturnide exactly as prescribed by your doctor. It is important to take Amturnide every day to control your blood pressure.
- Take Amturnide one time a day, at about the same time each day.
- Take Amturnide the same way every day, either with or without a meal.
- Your doctor may change your dose of Amturnide if needed. Do not change the amount of Amturnide you take without talking to your doctor.
- If you miss a dose of Amturnide, take it as soon as you remember. If it is close to your next dose, do not take the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time.
- If you take too much Amturnide, call your doctor or a Poison Control Center, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What are the dosage forms and brand names of this medicine?[edit | edit source]
This medicine is available in fallowing doasage form:
- As Tablets (aliskiren/ amlodipine/ HCTZ): 150/5/12.5, 300/5/12.5, 300/5/25, 300/10/12.5, 300/10/25 mg.
This medicine is available in fallowing brand namesː
- Amturnide
What side effects can this medication cause?[edit | edit source]
The most common side effects of this medicine include:
- swelling of your ankles, feet, and hands
- dizziness
- headache
- stuffy or runny nose and sore throat
Common side effects of Amturnide include:
- diarrhea
- cough
- tiredness
- high levels of potassium in the blood (hyperkalemia)
Amturnide may cause serious side effects, including:
- Harm to an unborn baby causing injury or death
- Angioedema
- hypotension
- Worsening chest pain or heart attack
- Allergic reactions
- Worsening of lupus
- hypokalemia
- Eye problems
What special precautions should I follow?[edit | edit source]
- Avoid concomitant use with ARBs or ACEI in patients with renal impairment (GFR<60 mL/min).
- Angioedema of the face, extremities, lips, tongue, glottis and/or larynx has been reported in patients treated with aliskiren and has necessitated hospitalization and intubation. Discontinue Amturnide.
- In patients with an activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, such as volume- and/or salt-depleted patients receiving high doses of diuretics, symptomatic hypotension may occur in patients receiving renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blockers. Correct volume depletion prior to initiation.
- Increased angina or myocardial infarction may occur upon dosage initiation or increase in amlodipine.
- Monitor renal function periodically in patients treated with Amturnide. Changes in renal function, including acute renal failure, can be caused by drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin system and by diuretics.
- Amturnide has not been studied in patients with heart failure.
- Hypersensitivity reactions to HCTZ may occur in patients with or without a history of allergy or bronchial asthma, but are more likely in patients with such a history.
- Thiazide diuretics have been reported to cause exacerbation or activation of systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Monitor serum potassium periodically in patients receiving aliskiren. Drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin system can cause hyperkalemia.
- Hydrochlorothiazide, a sulfonamide, can cause an idiosyncratic reaction, resulting in transient myopia and acute angle closure glaucoma.
What to do in case of emergency/overdose?[edit | edit source]
In case of overdose, call the poison control helpline of your country. In the United States, call 1-800-222-1222.
- Overdose related information is also available online at poisonhelp.org/help.
- In the event that the victim has collapsed, had a seizure, has trouble breathing, or can't be awakened, immediately call emergency services. In the United States, call 911.
Can this medicine be used in pregnancy?[edit | edit source]
- Amturnide can cause harm or death to an unborn baby.
- Talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your blood pressure if you plan to become pregnant.
- If you get pregnant while taking Amturnide, tell your doctor right away.
Can this medicine be used in children?[edit | edit source]
- It is not known if Amturnide is safe and works in children under 18 years of age.
What are the active and inactive ingredients in this medicine?[edit | edit source]
- Active ingredients: Aliskiren hemifumarate, amlodipine besylate, and HCTZ.
- Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hypromellose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide black, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethyleneglycol, povidone, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Who manufactures and distributes this medicine?[edit | edit source]
Distributed by: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation East Hanover, New Jersey
What should I know about storage and disposal of this medication?[edit | edit source]
- Store at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF) in original container.
- Protect from heat and moisture.
- Dispense in original container.
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
| Diuretics (C03) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Deepika vegiraju, Prab R. Tumpati, MD