Lupus
(Redirected from Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE))
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Lupus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Fatigue, joint pain, rash, fever |
| Complications | Kidney failure, heart disease, lung disease |
| Onset | Usually between ages 15 and 45 |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Autoimmune disease |
| Risks | Genetics, environmental factors, hormones |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests, urinalysis, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Immunosuppressive drugs, corticosteroids, antimalarial medication |
| Medication | Hydroxychloroquine, prednisone, methotrexate |
| Prognosis | Variable; can be life-threatening |
| Frequency | 20 to 70 per 100,000 people |
| Deaths | Approximately 1,000 per year in the US |
Lupus is derived from the Latin term for "wolf". In English, "lupus" can denote several references, such as:
- Diseases associated with the term include:
Lupus erythematosus, the autoimmune disease commonly referred to as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Lupus nephritis, which is inflammation triggered by SLE. Lupus pernio, a manifestation of sarcoidosis. Lupus vulgaris, linked with cutaneous tuberculosis.
- Other uses of the term are:
Lupus, an astronomical constellation. Lupus, a comic series by Frederik Peeters. Toshiba Brave Lupus, a semi-professional rugby team based in Japan.
Overview of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus)[edit | edit source]
Systemic lupus erythematosus (often abbreviated to lupus) is a complex disorder that can harm various body parts including the joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and the brain. It's not contagious, and its course varies among individuals. Those with lupus experience cycles of symptomatic periods (known as 'flares') and symptom-free periods ('remission').
What Happens in Lupus?[edit | edit source]
Lupus arises when the body's immune system, which ordinarily defends against infections, starts attacking its own tissues.
Who Is Affected?[edit | edit source]
While lupus affects both genders, it's more prevalent in women. It's especially common among African American women compared to Caucasian women and also frequently appears in Hispanic, Asian, and Native American women. Genetics play a role too, as lupus can be hereditary, although the likelihood is low.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
Systemic lupus erythematosus presents an array of symptoms, varying in severity from one person to the next. These can include:
- Joint pain or swelling.
- Persistent fever without any apparent cause.
- Fatigue.
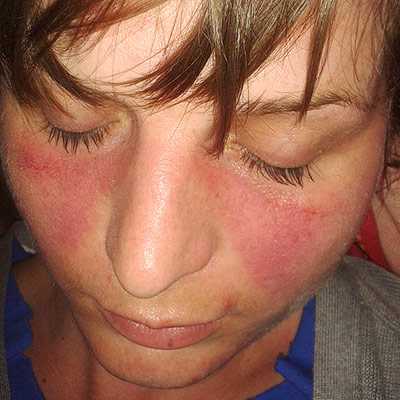
- Skin rashes, especially a "butterfly" rash on the face.
- Breathing pain.
- Hair loss.
- Photosensitivity.
- Oral ulcers.
- Color changes in fingers and toes due to cold or stress.
- Swelling in extremities or around the eyes.
Additional manifestations can encompass:
- Anemia.
- Kidney inflammation necessitating medication.
- Neurological symptoms like headaches, dizziness, and even seizures.
- Blood vessel inflammation.
- Abnormalities in blood cell counts.
- Increased clotting tendencies.
- Cardiac complications.
Causes[edit | edit source]
The exact etiology of SLE remains elusive but is believed to encompass genetic, environmental, hormonal, and possibly certain medicinal factors.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosing SLE is challenging and can span months or even years. It entails:
- Comprehensive medical history review.
- A detailed physical examination.
- Laboratory testing, especially looking for specific antibodies.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Modern treatments offer a multitude of options for managing lupus. Medications include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): For pain, fever.
- Antimalarials: For fatigue, joint pain, skin issues.
- Corticosteroids: Potent anti-inflammatory agents.
- Immunosuppressives: For severe cases affecting kidneys or the central nervous system.
- B-lymphocyte stimulator (BlyS)-specific inhibitors: Targeting specific immune cells.
Alternative treatments can also help with symptom relief.
Living With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus)[edit | edit source]
Dealing with a long-lasting disease like systemic lupus erythematosus (lupus) can be hard on the emotions. You might think that your friends, family, and coworkers do not understand how you feel. Sadness and anger are common reactions. Besides working with your doctor to determine a treatment plan, there are a few things you can do to help you live with lupus:
- Learn to recognize the warning signs of a flare so that you and your doctor might reduce or prevent them. These warning signs include:
- Increased tiredness.
- Pain.
- Rash.
- Fever.
- Stomach discomfort.
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
- Eat a proper diet, exercise, and learn relaxation techniques to help cope with stress. A healthy lifestyle, as well as quitting smoking, will also reduce your risk for heart disease associated with lupus. Talk to your doctor before starting an exercise program.
- Develop and maintain a good support system of family, friends, medical professionals, community organizations, and support groups.
Pregnancy and Contraception for Women With Lupus[edit | edit source]
Although pregnancy in women with lupus is considered high risk, most women with mild to moderate lupus can have healthy pregnancies. Regular care and good nutrition during pregnancy are essential. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Research shows that birth control pills do not increase the risk for severe flares among women with lupus. As a result, doctors are increasingly prescribing oral contraceptives to women with inactive or stable disease.
Outlook (Prognosis)[edit | edit source]
The outcome for people with SLE has improved in recent years. Many people with SLE have mild symptoms. How well you do depends on how severe the disease is. Most people with SLE will require medicines for a long time. Nearly all will require hydroxychloroquine indefinitely.
Possible Complications[edit | edit source]
LUPUS NEPHRITIS Some people with SLE have abnormal immune deposits in the kidney cells. This leads to a condition called lupus nephritis. People with this problem may develop kidney failure. They may need dialysis or a kidney transplant. A kidney biopsy is done to detect the extent of damage to the kidney and to help guide treatment. If active nephritis is present, treatment with immunosuppressive medicines including high doses of corticosteroids along with either cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate are needed. OTHER PARTS OF THE BODY SLE can cause damage in many different parts of the body, including:
- Blood clots in arteries of veins of the legs, lungs, brain, or intestines
- Destruction of red blood cells or chronic anemia.
- Fluid around the heart (pericarditis), or inflammation of the heart (myocarditis or endocarditis)
- Fluid around the lungs and damage to lung tissue
- Pregnancy problems, including miscarriage
- Stroke
- Bowel damage with abdominal pain and obstruction
- Inflammation in the intestines
- Severely low blood platelet count (platelets are needed to stop any bleeding)
- Inflammation of the blood vessels
SLE and Pregnancy[edit | edit source]
Both SLE and some of the medicines used for SLE can harm an unborn child. Talk to your provider before you become pregnant. If you become pregnant, find a provider who is experienced with lupus and pregnancy.
Lupus nephritis[edit | edit source]
- Minimal mesangial glomerulonephritis Class I (Minimal mesangial glomerulonephritis Minimal mesangial glomerulonephritis)
- Mesangial proliferative lupus nephritis Class II (Mesangial proliferative lupus nephritis Mesangial proliferative lupus nephritis)
- Focal proliferative nephritis Class III (Focal proliferative nephritis Focal proliferative nephritis)
- Diffuse proliferative nephritis Class IV (Diffuse proliferative nephritis Diffuse proliferative nephritis)
- Membranous glomerulonephritis Class V (Membranous glomerulonephritis Membranous nephritis)
- Glomerulosclerosis Class VI (Glomerulosclerosis Glomerulosclerosis)
| Lupus nephritis |
|---|
|
|
| Diseases of the skin and appendages by morphology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Dermatitis and eczema | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Systemic connective tissue disorders | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Hypersensitivity and autoimmune diseases (279.5–6) | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD




