4-AcO-DMT
A synthetic psychedelic compound
| 4-AcO-DMT | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | Oral, Insufflation, Intravenous |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | Unscheduled |
| CAS Number | 92292-84-7 |
| PubChem | 443378 |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | 391759 |
| KEGG | |
4-Acetoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (4-AcO-DMT) is a synthetic psychedelic compound that is structurally related to psilocybin, the active ingredient in magic mushrooms. It is a member of the tryptamine class of compounds and is known for its psychedelic effects, which are similar to those of psilocin and DMT.
Chemical Structure and Properties[edit | edit source]
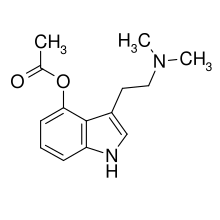
4-AcO-DMT is the acetylated form of psilocin, which is the active metabolite of psilocybin. Its chemical structure consists of an indole ring, which is a common feature of tryptamines, with an acetoxy group at the 4-position and a dimethylaminoethyl side chain. The molecular formula of 4-AcO-DMT is C14H18N2O2.
Pharmacology[edit | edit source]
4-AcO-DMT is believed to act as a prodrug to psilocin, meaning that it is metabolized in the body to produce psilocin, which then exerts its effects on the brain. Psilocin primarily acts as a partial agonist at the 5-HT2A receptor, which is a subtype of the serotonin receptor. This interaction is thought to be responsible for the psychedelic effects of 4-AcO-DMT.
Effects[edit | edit source]
The effects of 4-AcO-DMT are similar to those of psilocybin and DMT, and can include:
- Altered perception of time and space
- Visual and auditory hallucinations
- Enhanced introspection and emotional experiences
- Altered thought processes
- Euphoria
The onset of effects typically occurs within 20 to 40 minutes when taken orally, with the peak effects lasting for 2 to 4 hours, and the total duration of effects lasting 4 to 6 hours.
Legal Status[edit | edit source]
The legal status of 4-AcO-DMT varies by country. In some jurisdictions, it is considered a controlled substance, while in others it remains unscheduled. It is important to check local laws and regulations regarding its use and possession.
Research and Use[edit | edit source]
4-AcO-DMT has been used in psychedelic research to study its effects on the brain and its potential therapeutic applications. Some researchers are interested in its potential to treat conditions such as depression, anxiety, and PTSD. However, more research is needed to fully understand its safety and efficacy.
Also see[edit | edit source]
| Tryptamines |
|---|
|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


