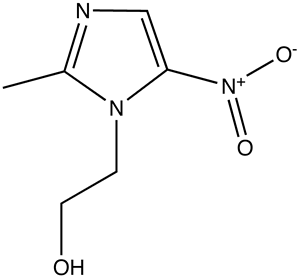
Metronidazole
(Redirected from Metronidazole hydrochloride)
What is Metronidazole?[edit | edit source]
- Metronidazole (Flagyl; Flagyl 375; Flagyl ER) is a nitroimidazole, exerts antibacterial effects widely used in the treatment of many anaerobic and certain protozoan and parasitic infections.
What are the uses of this medicine?[edit | edit source]
Metronidazole (Flagyl; Flagyl 375; Flagyl ER) is used in the treatment of:
- Symptomatic Trichomoniasis
- Asymptomatic Trichomoniasis
- Treatment of Asymptomatic Consorts
- Amebiasis
Anaerobic Bacterial Infections such as:
- Intra-Abdominal Infections, including peritonitis, intra-abdominal abscess, and liver abscess
- Skin and Skin Structure Infections
- Gynecologic Infections, including endometritis, endomyometritis, tubo-ovarian abscess, and post-surgical vaginal cuff infection
- Bacterial Septicemia
- Bone and Joint Infections, as adjunctive therapy
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Infections, including meningitis and brain abscess
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infections, including pneumonia, empyema, and lung absces
- Endocarditis
- Metronidazole extended-release (long-acting) tablets are used to treat bacterial vaginosis (an infection caused by too much of certain types of harmful bacteria in the vagina) in women.
How does this medicine work?[edit | edit source]
- Metronidazole (met" roe nid' a zole) is a nitroimidazole antibiotic that is activated by reduction of its nitro group by susceptible organisms.
- The activated form of metronidazole is a highly reactive radical anion which targets and damages large protein molecules and DNA.
- Mammalian cells do not ordinarily activate metronidazole, which accounts for its lack of toxicity in humans.
- Once metronidazole enters the organism by passive diffusion and activated in the cytoplasm of susceptible anaerobic bacteria, it is reduced; this process includes intracellular electron transport proteins such as ferredoxin, transfer of an electron to the nitro group of the metronidazole, and formation of a short-lived nitroso free radical.
- Because of this alteration of the metronidazole molecule, a concentration gradient is created and maintained which promotes the drug’s intracellular transport.
- The reduced form of metronidazole and free radicals can interact with DNA leading to inhibition of DNA synthesis and DNA degradation leading to death of the bacteria.
- The precise mechanism of action of metronidazole is unclear.
- Metronidazole has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following bacteria:
Gram-positive anaerobes:
- Clostridium species
- Eubacterium species
- Peptococcus species
- Peptostreptococcus species
Gram-negative anaerobes:
- Bacteroides fragilis group ( B. fragilis, B. distasonis, B. ovatus, B. thetaiotaomicron, B.vulgatus)
- Fusobacterium species
- Protozoal parasites
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Trichomonas vaginalis
Who Should Not Use this medicine ?[edit | edit source]
This medicine cannot be used in:
- patients with a prior history of hypersensitivity to metronidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives.
- patients with trichomoniasis, metronidazole tablets are contraindicated during the first trimester of pregnancy.
- patients who have taken disulfiram within the last two weeks.
- patients consuming alcohol or products containing propylene glycol during and for at least three days after therapy with metronidazole.
- patients with Cockayne syndrome.
What drug interactions can this medicine cause?[edit | edit source]
- Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Be sure to mention any of the following:
- anticoagulants ('blood thinners') such as warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven), busulfan (Busulfex, Myleran), cimetidine (Tagamet HB), lithium (Lithobid), phenobarbital, and phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek).
Is this medicine FDA approved?[edit | edit source]
- Metronidazole was approved for use in the United States in 1963 and currently several million prescriptions are filled yearly.
How should this medicine be used?[edit | edit source]
Recommended dosage: For Trichomoniasis:
- One-day treatment:Two grams of metronidazole tablets, given either as a single dose or in two divided doses of one gram each, given in the same day.
- Seven-day course of treatment:250 mg three times daily for seven consecutive days.
For Amebiasis:
In Adults:
- For acute intestinal amebiasis (acute amebic dysentery): 750 mg orally three times daily for 5 to 10 days.
- For amebic liver abscess: 500 mg or 750 mg orally three times daily for 5 to 10 days.
In Pediatric patients:
- 35 to 50 mg/kg/24 hours, divided into three doses, orally for 10 days.
For Anaerobic Bacterial Infections:
- The usual adult oral dosage is 7.5 mg/kg every six hours (approx. 500 mg for a 70-kg adult).
- A maximum of 4 g should not be exceeded during a 24-hour period.
- The usual duration of therapy is 7 to 10 days; however, infections of the bone and joint, lower respiratory tract, and endocardium may require longer treatment.
In Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment:
- The dose of metronidazole tablets should be reduced by 50%.
Metronidazole extended-release tablets: For Bacterial Vaginosis:
- 750 mg once daily by mouth for seven consecutive days.
Administration:
- Metronidazole comes as a tablet, an extended-release tablet, and as a capsule to take by mouth.
- Metronidazole capsules and tablets are usually taken as a one-time dose (or divided into two doses on 1 day) or two to four times daily for up to 10 days or longer.
- Metronidazole extended-release tablets are usually taken once daily at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal for 7 days.
- Swallow the extended-release tablets whole; do not split, chew, or crush them.
- Continue to take this medication even if you feel well.
- Do not stop taking it without talking to your doctor.
- If you stop taking this medication too soon or skip doses, your infection may not be completely treated and the bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.
What are the dosage forms and brand names of this medicine?[edit | edit source]
This medicine is available in fallowing doasage form:
- As as a tablet, an extended-release tablet, and as a capsule
- Other formulations include injectable solutions, extended release tablets, suppositories, and topical creams.
This medicine is available in fallowing brand namesː
- Flagyl; Flagyl 375; Flagyl ER
What side effects can this medication cause?[edit | edit source]
The most common side effects of this medicine include: Central Nervous System:
- convulsive seizures, encephalopathy, aseptic meningitis, optic and peripheral neuropathy, headache, syncope, dizziness, vertigo, incoordination, ataxia, confusion, dysarthria, irritability, depression, weakness, and insomnia.
Gastrointestinal:
- nausea, sometimes accompanied by headache, anorexia, and occasionally vomiting; diarrhea; epigastric distress; and abdominal cramping and constipation.
Mouth:
- A sharp, unpleasant metallic taste is not unusual. Furry tongue, glossitis, and stomatitis.
Dermatologic:
- Erythematous rash and pruritus.
Hematopoietic:
- Reversible neutropenia (leukopenia); rarely, reversible thrombocytopenia.
Cardiovascular:
Hypersensitivity:
- Urticaria, erythematous rash, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, flushing, nasal congestion, dryness of the mouth (or vagina or vulva), and fever.
Renal:
- Dysuria, cystitis, polyuria, incontinence, and a sense of pelvic pressure.
Hepatic:
- Cases of severe irreversible hepatotoxicity/acute liver failure, including cases with fatal outcomes with very rapid onset after initiation of systemic use of metronidazole, have been reported.
Other:
- Proliferation of Candida in the vagina, dyspareunia, decrease of libido, proctitis, and fleeting joint pains sometimes resembling “serum sickness.”
What special precautions should I follow?[edit | edit source]
- Cases of encephalopathy and peripheral neuropathy (including optic neuropathy) have been reported with metronidazole.
- Convulsive seizures have been reported in patients treated with metronidazole.
- Cases of aseptic meningitis have been reported with metronidazole.
- Patients with hepatic impairment metabolize metronidazole slowly, with resultant accumulation of metronidazole in the plasma. For patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, no dosage adjustment is needed but these patients should be monitored for metronidazole associated adverse events.
- Previously unrecognized candidiasis may present more prominent symptoms during therapy with metronidazole and requires treatment with a candidacidal agent.
- Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole and should be used with caution in patients with evidence of or history of blood dyscrasia. Total and differential leukocyte counts are recommended before and after therapy.
- Prescribing metronidazole in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial or parasitic infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria and parasites.
- Discontinue consumption of alcoholic beverages or products containing propylene glycol while taking metronidazole and for at least three days afterward because abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and flushing may occur.
- Patients should be counseled that metronidazole should only be used to treat bacterial and parasitic infections. Metronidazole does not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold).
- When metronidazole is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by metronidazole in the future.
- Metronidazole is present in human milk. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. Alternatively, a nursing mother may choose to pump and discard human milk for the duration of metronidazole therapy, and for 24 hours after therapy ends and feed her infant stored human milk or formula.
- Metronidazole has been linked to rare instances of acute, clinically apparent liver injury.
What to do in case of emergency/overdose?[edit | edit source]
Symptoms of overdose may include:
- nausea, vomiting, and ataxia
- Neurotoxic effects, including seizures and peripheral neuropathy, have been reported.
Management of overdosage:
- In case of overdose, call the poison control helpline of your country. In the United States, call 1-800-222-1222.
- Overdose related information is also available online at poisonhelp.org/help.
- In the event that the victim has collapsed, had a seizure, has trouble breathing, or can't be awakened, immediately call emergency services. In the United States, call 911.
- There is no specific antidote for metronidazole overdose; therefore, management of the patient should consist of symptomatic and supportive therapy.
Can this medicine be used in pregnancy?[edit | edit source]
- There are no adequate and well controlled studies of metronidazole in pregnant women.
- Most studies did not show an increased risk for congenital anomalies or other adverse fetal outcomes following metronidazole exposure during pregnancy.
Can this medicine be used in children?[edit | edit source]
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established, except for the treatment of amebiasis.
What are the active and inactive ingredients in this medicine?[edit | edit source]
Active ingredient:
- metronidazole
Inactive ingredients:
- silicified microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, colloidal silicon dioxide and hydrogenated vegetable oil.
Who manufactures and distributes this medicine?[edit | edit source]
Extended-release tablets:
Manufactured by:
- Alembic Pharmaceuticals Limited
- (Formulation Division),
- Village Panelav, P. O. Tajpura, Near Baska,
- Taluka-Halol, Panchmahal, Gujarat, India.
What should I know about storage and disposal of this medication?[edit | edit source]
- Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
- PROTECT FROM LIGHT.
- Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
| Stomatological preparations (A01) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Antibiotics and chemotherapeutics for dermatological use (D06) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Gynecological anti-infectives and antiseptics (G01) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Antibacterials that inhibit nucleic acid (J01E, J01M) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Antiparasitics – antiprotozoal agents – Chromalveolata antiparasitics (P01) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Antiparasitics directed at excavata parasites (P01) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Antiparasitics – antiprotozoal agents – agents against amoebozoa/amebicide (P01) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP1 injections from $125
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program NYC and a clinic to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our W8MD's physician supervised medical weight loss centers in NYC provides expert medical guidance, and offers telemedicine options for convenience.
Why choose W8MD?
- Comprehensive care with FDA-approved weight loss medications including:
- loss injections in NYC both generic and brand names:
- weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion etc.
- Accept most insurances for visits or discounted self pay cost.
- Generic weight loss injections starting from just $125.00 for the starting dose
- In person weight loss NYC and telemedicine medical weight loss options in New York city available
- Budget GLP1 weight loss injections in NYC starting from $125.00 biweekly with insurance!
Book Your Appointment
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss, and Philadelphia medical weight loss Call (718)946-5500 for NY and 215 676 2334 for PA
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD