Dextromethorphan
(Redirected from Dxm)
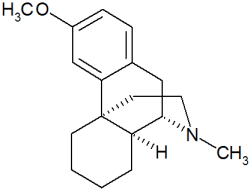
Dextromethorphan (DXM) is a medication commonly used as a cough suppressant in over-the-counter cold and cough medicines. It is available in various forms, including syrup, tablet, spray, and lozenge. DXM belongs to the morphinan class of medications and exhibits sedative, dissociative, and stimulant properties at lower doses. Unlike typical morphinan compounds, dextromethorphan does not have a significant affinity for the mu-opioid receptor activity and exerts its therapeutic effects through several other receptors. In its pure form, dextromethorphan occurs as a white powder.
Uses[edit | edit source]
Dextromethorphan is primarily used as a cough suppressant to provide temporary relief from nonproductive coughs caused by various respiratory conditions, such as the common cold, bronchitis, and allergies. It is often combined with other medications, such as decongestants, antihistamines, and analgesics, in multi-symptom cold and cough formulations.
Mechanism of Action[edit | edit source]
DXM's primary mechanism of action involves its activity as an NMDA receptor antagonist, which helps to suppress the cough reflex. It also interacts with other receptors, such as the sigma-1 receptor and the serotonin transporter. These interactions contribute to the drug's sedative, dissociative, and stimulant effects.
Side Effects and Precautions[edit | edit source]
Common side effects of dextromethorphan include dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting. Some individuals may experience more severe side effects, such as allergic reactions, difficulty breathing, or hallucinations. It is important to follow the recommended dosing instructions and avoid consuming excessive amounts of DXM, as high doses can lead to serious side effects, including respiratory depression, seizures, and death.
Individuals who are taking certain medications, such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), should avoid using dextromethorphan due to the risk of dangerous drug interactions. Pregnant or breastfeeding women and those with liver or kidney disease should consult with their healthcare provider before using DXM-containing products.
Recreational Use and Abuse[edit | edit source]
Dextromethorphan has been subject to recreational abuse due to its dissociative and hallucinogenic effects at high doses. This has led to the emergence of a subculture of users who consume DXM recreationally, often referred to as "dexing" or "robotripping." The abuse of DXM can have serious health risks, including addiction, long-term cognitive impairment, and even death. To curb recreational use, some countries and jurisdictions have implemented age restrictions or behind-the-counter policies for the sale of DXM-containing products.
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
| Pharmacodynamics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
|
| Cough and cold preparations (R05) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD